The main result of the monetarist model is that
A) the economy is slow to adjust to sticky wages and prices.
B) workers and firms have rational expectations.
C) the quantity of money should be increased at a constant rate.
D) productivity shocks explain fluctuations in real GDP.
C
You might also like to view...
Pedro's utility of wealth is 6 units for $10,000 and 10 units for $20,000. A friend gave him a lottery ticket for his birthday. The ticket won, giving him either $10,000 with probability 0.5 or $20,000 with probability 0.5
Pedro's expected utility from the lottery ticket is A) between 6 and 8 units. B) equal to 8 units. C) between 8 and 10 units. D) equal to 10 units.
Natural monopolies form when
a. small firms merge to form larger firms b. one firm has control over the entire supply of a basic input required to produce the product c. one firm's monopoly position is created and enforced by the government d. one firm receives patent protection for certain basic production processes e. long-run average cost declines as a firm expands output
Central banks that have a hierarchical mandate with inflation targeting basically are saying:
A. hitting the inflation target comes first, everything else comes second. B. the inflation target is the second most important goal after economic growth, which is always the most important goal for monetary policymakers. C. hitting the inflation target is the only objective. D. hitting the inflation target is the first priority after all other stated objectives are reached.
Refer to the below table. If the firms are playing a sequential game, then
Answer the question based on the following payoff matrix for a duopoly in which the numbers indicate the profit from either opening a coffee shop in a small town or not opening the coffee shop.
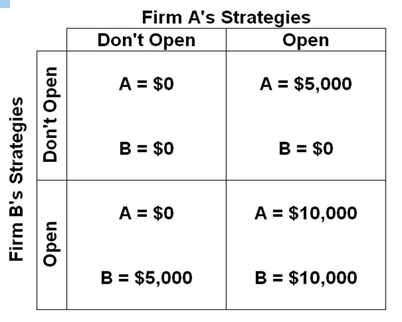
A. There is a dominant strategy for this game.
B. There is only one Nash equilibrium for this game.
C. There are two potential Nash equilibrium for this game.
D. Both firms will choose not to open a coffee shop.