Refer to the information provided in Figure 26.6 below to answer the question(s) that follow.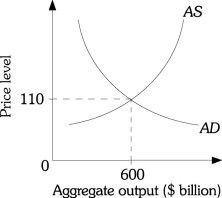 Figure 26.6Refer to Figure 26.6. Suppose the equilibrium price level is 110. An increase in the supply of oil would probably
Figure 26.6Refer to Figure 26.6. Suppose the equilibrium price level is 110. An increase in the supply of oil would probably
A. decrease both the equilibrium output and the price level.
B. increase the equilibrium output and decrease the price level.
C. decrease the equilibrium output and increase the price level.
D. increase both the equilibrium output and the price level.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The Celler-Kefauver Act made it illegal to:
a. provide selective discounts. b. set prices below marginal cost. c. conspire to collude. d. buy with cash a competitor's patents, plants, or equipment. e. price discriminate.
Credit risk is:
A. the risk of a borrower defaulting on a loan. B. lower, the longer the length of the loan. C. lower, the larger the amount of the loan. D. the risk of not being able to get a loan when your credit is good.
Which of the following grew rapidly after the passage of the Medicare and Medicaid programs in the mid-1960s?
a. the share of healthcare expenditures financed directly by the consumer b. the share of healthcare expenditures financed by third parties c. the prices of healthcare relative to the prices of other goods and services d. both b and c
Which statement is true?
A. The Fed failed to perform its lender of last resort job after the emergency created by the terrorist attacks on 9/11. B. Thanks to the Check Clearing for the 21st Century Act, the use of checks as a medium of exchange should disappear within a few years. C. The Chinese government and central bank has a significant influence over long-term interest rates in the U.S. D. The Fed changes the federal funds rate in exactly the same manner in which it changes the discount rate.