Fiscal policy can act just like monetary policy to offset shifts in the dynamic aggregate demand curve and stabilize inflation and output. Explain how the two policies could have the same effect.
What will be an ideal response?
Fiscal policy consists of changes in taxes and/or government spending. An increase in taxes or a decrease in government spending results in a decrease in aggregate expenditure, similar to a monetary policy that resulted in higher interest rates. A decrease in taxes or an increase in government spending results in an increase in aggregate expenditure, similar to a monetary policy that lowered interest rates. Put simply, both policies can be used to effect changes in aggregate demand to provide stimulus or cool off the economy in the context of other changes that are occurring.
You might also like to view...
The players of prisoner's dilemma-type games:
A. would be much better off if they could cooperate. B. have an incentive to never cooperate. C. have a dominant strategy to never cooperate. D. All of these statements are true.
If Cov(z,x) ? 0, then z and x are correlated.?
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
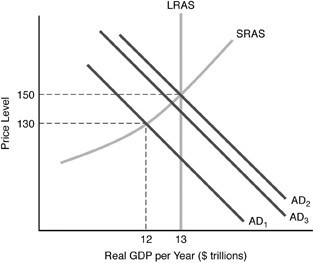 Refer to the above figure. Suppose that the economy starts at AD1. If the government reduces taxes, then the economy goes to AD2, but then falls back to AD3. This is an example of
Refer to the above figure. Suppose that the economy starts at AD1. If the government reduces taxes, then the economy goes to AD2, but then falls back to AD3. This is an example of
A. partial crowding-out effect. B. Ricardian equivalence. C. complete crowding-out effect. D. laissez-faire.
Refer to the information provided in Scenario 25.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.SCENARIO 25.1: The following table shows the changes in deposits, reserves, and loans of 4 banks as a result of a $100,000 initial deposit in Bank No. 1. Assume all banks are loaned up.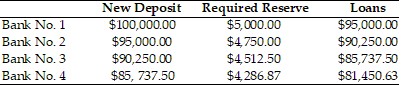 Refer to Scenario 25.1. What is the money multiplier in this economy?
Refer to Scenario 25.1. What is the money multiplier in this economy?
A. 10 B. 16.67 C. 20 D. 50