Javier is a member of a teachers union. The union recently failed to secure a wage increase as part of a new agreement. Instead, the wage will remain roughly 5 percent higher than comparable jobs in the nonunion sector. How will this affect Javier’s job security?
a. His job security will not change much because keeping wages constant will not create
changes in demand for or supply of labor.
b. His job will be less secure because the collective bargaining failure shows declining
demand for teachers.
c. His job will be more secure because it will drive many of the union teachers to find
nonunion jobs.
d. His job will be less secure because the announcement will lead to a large influx of
nonunion teachers.
a. His job security will not change much because keeping wages constant will not create
changes in demand for or supply of labor.
You might also like to view...
Why is the price of a scarce exhaustible resource in a competitive market above the marginal cost of providing a unit of the resource?
What will be an ideal response?
The equilibrium compensating wage differential between two occupations in the same city is $10 per hour. Both occupations have equivalent training requirements. Shannon works in the higher-paying occupation and would have been willing to do so even if the compensating differential was $5 per hour. Therefore,
a. Shannon will migrate to the lower-paying occupation b. Shannon must have a greater distaste than the typical worker for the nonmonetary characteristics of her occupation c. the equilibrium compensating wage differential is more than enough to prevent Shannon from moving to the other job d. the higher-paying occupation cannot have a perfectly competitive labor market e. Shannon must have a greater preference than the typical worker for the lower- paying occupation
Based on the graphic for perfect competition versus monopoly, the welfare for perfect competition is ______ the welfare for monopoly.
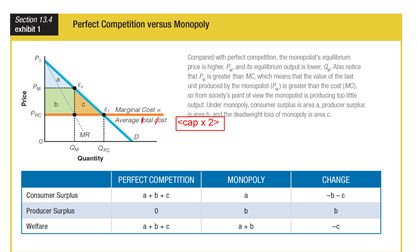
a. greater than
b. less than
c. equal to
d. the opposite of
Which of the following is least likely to induce precautionary saving?
a) the decision to retire from work at age 62 b) the possibility of being laid-off from work c) the uncertainty of one’s lifetime d) the risk of becoming ill e) the prospect of a potentially large tax increase in the future