If a perfectly competitive firm's total revenue is less than its total variable cost, the firm
A) should raise its price above its average variable cost.
B) should continue to produce and increase its demand.
C) should stop production by shutting down temporarily.
D) should adopt new technology in order to lower its costs of production.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Suppose the country of Dingo experienced an economic trough in January 2011. We can conclude that
A) real GDP in Dingo was increasing in January 2011. B) an expansion occurred after January 2011. C) Dingo did not experience a recession in 2010. D) Dingo's potential GDP fell in 2011.
Great Benefit is a health insurance company with two types of customers: healthy persons and sickly persons. A healthy person has 1-to-5 odds of getting ill, and a sickly person has 1-to-1 odds of getting ill. However, the insurance company cannot distinguish between healthy and sickly persons. Brett is a risk-averse person who purchases health insurance from Great Benefit. Without insurance, Brett's income will be $8,000 if he remains healthy and $2,000 if he becomes ill. Brett's situation is diagrammed below.
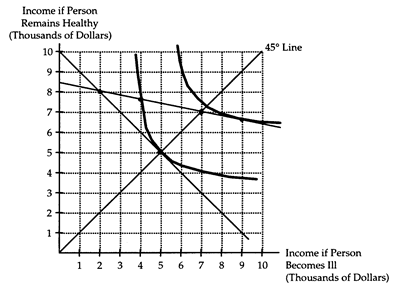
(i) Is Brett a healthy person or a sickly person? How can you tell?
(ii) Suppose Great Benefit offers two policies-one at fair odds for healthy persons and one at fair odds for sickly persons-that can be purchased in unlimited quantities. What type of policy and how much insurance will Brett choose to purchase?
(iii) What type of information problem does the insurance company face? What limit should the insurance company place on insurance at "healthy" odds to deal with this problem?
In the aggregate demand/aggregate supply model, an increase in a country's sustainable potential output is represented by
a. an increase in aggregate demand. b. a decrease in aggregate demand. c. an increase in long-run aggregate supply. d. an increase in the general level of prices.
The concept of relative poverty
A. leads to the concept of inequality. B. replaces the need for concepts of absolute poverty. C. is measured relative to the poverty line. D. is only relevant in low income countries.