Absolute advantage is
A) the ability to produce a good or service at a higher opportunity cost than one's competitors.
B) the ability to produce more of a good or service than competitors that have fewer resources.
C) the ability to produce more of a good or service than competitors when using the same amount of resources.
D) the ability to produce higher quality goods compared to one's competitors.
C
You might also like to view...
If a tax on 5 cents a tomato lowers the price received by tomato sellers by 5 cents a tomato , then the supply of tomatoes is perfectly ___ and the seller pays ____
A) inelastic; all B) elastic; all C) inelastic; some of D) inelastic; none of E) elastic; none of
Consider the game depicted below. Player 1 decides between going L or R in stage 1 and 3 of the game. Player 2 decides between going l and r in stage 2 of the game.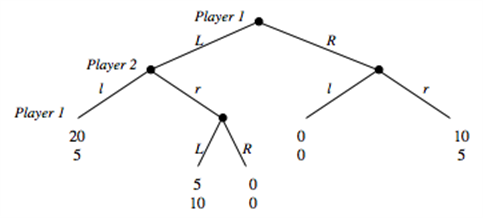
c. Identify the subgame perfect equilibrium strategies and outcome. d. Identify the Nash Equilibria that are not subgame perfect. e. For each Nash Equilibrium that is not subgame perfect, explain which parts of the Nash Equilibrium strategies are non-credible. f. Suppose you have developed a drug that can be administered without the victim being aware of it. The effect of the drug is that the victim suddenly becomes gullible and believes anything he is told. You only have 1 dose of the drug and decide to auction it off to the two players right before they play each other in the game you have analyzed so far. Each player is asked to submit a sealed bid, and the highest bidder will be sold the drug at a price equal to the highest bid. In case of a tie in bids, a coin is flipped to determine who wins and pays the price that was bid. Suppose in this part that payoffs are in terms of dollars and that bids can be made in one cent increments. Suppose further that players do not consider bidding above the maximum they are willing to pay. Given that the players know each other's payoffs in the above game, what is the equilibrium price that you will be able to sell the drug for? (Hint: There are two possible answers.) g. In part (f), we said "Suppose further that players do not consider bidding above the maximum they are willing to pay." Can you think of a Nash equilibrium to the auction that would end in a price of $8 if we had not made that statement in (f)? What will be an ideal response?
Refer to Figure 5-7. Which of the following statements is true?
A) The optimal quantity of pollution reduction is QB. B) The optimal quantity of pollution reduction is QE. C) At QE the benefits of reducing pollution outweigh the cost of pollution reduction. D) At QB society is under allocating resources to pollution reduction.
An unplanned increase in inventories results from
A) actual investment that is less than planned investment. B) an increase in planned investment. C) a decrease in planned investment. D) actual investment that is greater than planned investment.