If a tax on 5 cents a tomato lowers the price received by tomato sellers by 5 cents a tomato , then the supply of tomatoes is perfectly ___ and the seller pays ____
A) inelastic; all
B) elastic; all
C) inelastic; some of
D) inelastic; none of
E) elastic; none of
Answer: inelastic .. all
You might also like to view...
Fuji and Kodak produce identical film. The market demand for film is given by P = 8 - Q, where P is the price (in dollars per roll of film) and Q is the quantity (in hundreds of rolls). Each firm has the option of producing 150, 200, or 300 rolls of film at a constant marginal cost of $2 per roll with no fixed costs. The firms' possible profits for various outcomes are summarized in the accompanying table.
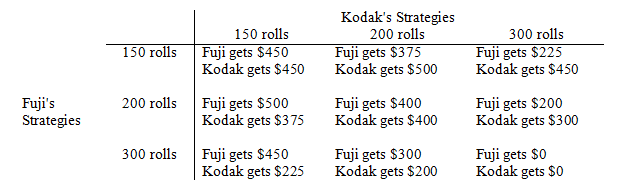
(i) If the two firms behave competitively, what will be the outcome of this game? Is this outcome Pareto optimal for the firms?
(ii) If the two firms merge and form a monopoly, what will be the outcome of this game? Is this outcome Pareto optimal for the firms?
(iii) What is the Nash equilibrium for this game? Is it Pareto optimal for the firms? How does it compare with the competitive and monopoly outcomes?
(iv) Suppose this game is played sequentially, with Fuji as the first player. What will be the Stackelberg equilibrium? Is it Pareto optimal?
Government assistance to workers whose employment prospects have worsened is called:
A. the minimum wage. B. worker mobility payments. C. transition aid. D. social security.
If the Fed has announced that it plans on increasing the interest rate it will
A) engage in contractionary open market operations, thereby decreasing the money supply. B) engage in expansionary open market operations, thereby decreasing the money supply. C) engage in expansionary open market operations, thereby increasing the money supply. D) engage in contractionary open market operations, thereby increasing the money supply.
What are the two principles of fairness that are applied to tax systems?
What will be an ideal response?