Which of the following is true of perfectly competitive firms?
a. For a perfectly competitive firm, as long as the price derived from expanded output exceeds the marginal cost of that output, the expansion of output creates additional economic profits.
b. Producing at the profit-maximizing output level means that a firm is actually earning economic profits
c. A competitive firm earning zero economic profit will be unable to continue in operation over time.
d. A perfectly competitive firm will operate in the short run only at price levels greater than or equal to average total costs.
a
You might also like to view...
Refer to Negative Externality. Suppose there is no attempt to internalize the externality. Pigovian analysis indicates that the externality creates a deadweight loss equal to
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the effects of a negative externality created by an industry's production. The equilibrium quantity in the absence of any attempt to internalize the externality is QE, and the optimal quantity according to a Pigovian analysis is QO.
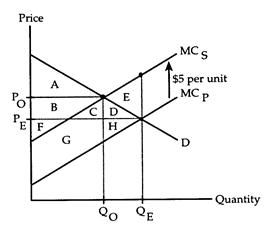
a. area C + D + E + G + H.
b. area D + E + H.
c. area C + D + G + H.
d. area E.
On a traditional supply and demand diagram,
a. price is measured along the horizontal axis and quantity along the vertical axis. b. price is measured along the vertical axis and quantity along the horizontal axis. c. quantity demanded is measured along the horizontal axis, quantity supplied is measured along the vertical axis, and price is indicated on the contour lines. d. quantity is measured along both axes and price is indicated on the contour lines.
What does it mean if a person makes a "decision at the margin"?
A) The person compares additional benefits and additional costs when deciding what to do. B) The person weighs the good against the bad and then decides what to do. C) The person is more likely to say yes than to say no. D) The person compares marginal benefits and total costs and then decides what to do. E) The person makes a decision based on a condition.
In answering which of the following questions would you find it necessary to calculate a present value?
a. Should Jane put $1,000 today into a 5-year certificate of deposit that pays 4 percent annual interest? b. Should ABC Corporation buy a factory today for $2 million, knowing that the factory will yield the corporation $3 million after 5 years? c. If Jill puts $5,000 today into a bank account that pays 3 percent interest, then how much will she have in the account after 2 years? d. You would find it necessary to calculate a present value in order to answer all of these questions.