Assume a two-country, two-commodity, two-input model where the following relationships hold:(K/L)U.S. > (K/L)ROW (K/L)automobiles > (K/L)shoes (K/L)U.S. is the capital-labor ratio in the United States, (K/L)ROW is the capital-labor ratio in the Rest of the World, (K/L)automobiles indicates the capital-labor ratio in the production of automobiles, and (K/L)shoes indicates the capital-labor ratio in the production of shoes.Assume further that technology and tastes are the same in the United States and the Rest of the World. The relationships shown in here indicate that the United States has a comparative advantage in the production of ________ while the Rest of the World has a comparative advantage in the production of
A. neither shoes nor automobiles; both goods
B. shoes; automobiles
C. automobiles; shoes
D. both the goods; neither shoes nor automobiles
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
An expected increase in the market price of oil in the coming year is likely to:
A) shift the supply curve of oil to the right in the current year. B) shift the demand curve for oil to the left in the current year. C) cause no changes in the demand and supply curves of oil in the current year. D) shift the supply curve of oil to the left in the current year.
If Chad's labor-supply curve is upward-sloping, then, for Chad,
a. an increase in the wage creates an income effect that is greater than the substitution effect. b. an increase in the wage creates a substitution effect that is greater than the income effect. c. leisure and consumption are perfect substitutes. d. leisure and consumption are perfect complements.
Player 1 and Player 2 are playing a game in which Player 1 has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Player 1 has chosen either Up or Down, Player 2, who can see what Player 1 has chosen, must choose Up or Down at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch.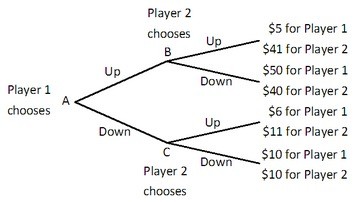 What is the equilibrium outcome of this game?
What is the equilibrium outcome of this game?
A. Player 1 and Player 2 both choose Down. B. Player 1 chooses Up and Player 2 chooses Down. C. Player 1 chooses Down and Player 2 chooses Up. D. Player 1 and Player 2 both choose Up.
At market equilibrium
A) demand equals supply. B) quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. C) surpluses are greater than shortages. D) shortages are greater than surpluses.