The simple case of pricing with market power assumes that (a) all consumers are charged the same price, (b) the firm sells one product, (c) demand exists in one time period, and (d) competitors do not pursue pricing games. Economists insist on reviewing what happens as each assumption is relaxed one at a time. But it is clear that in the real world all four are relaxed simultaneously. Why does economic analysis insist on such an unrealistic analysis?
What will be an ideal response?
The use of models provides an opportunity to perform careful thought experiments examining cause and effect. Economic analysis that looks at the effects of changing or relaxing one assumption at a time, holding other factors constant, lets us examine how just that one factor affects the determination of price in the real world. The use of models, simplified versions of the real world, provides a better understanding of the role of each of these factors.
You might also like to view...
When economists say that the demand for labor is a derived demand, they mean that it is
A. related to the demand for the product or service labor is producing. B. based on the assumption that workers are trying to maximize their money incomes. C. dependent on government expenditures for public goods and services. D. based on the desire of businesses to exploit labor by paying below equilibrium wage rates.
Foreign exchange means
a. changing dollars into foreign currency b. domestic currency held to finance international trade c. foreign currency d. trade between governments e. trade between individuals in different countries
When Ryan has an income of $2,000 . he consumes 30 units of good A and 50 units of good B. After Ryan's income decreases to $1,500, he consumes 23 units of good A and 55 units of good B. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Both goods A and B are normal goods. b. Both goods A and B are inferior goods. c. Good A is a normal good, and good B is an inferior good. d. Good A is an inferior good, and good B is a normal good.
The net (after tax) profit will be
Consider the following production function for a delivery service.
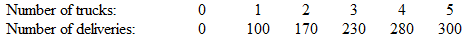
Each delivery generates $200 in gross revenue, and the tax rate is 10 percent on profits. Each truck costs $11,000.
a) $4,500
b) $8,100
c) $10,800
d) $11,700
e) $12,400