Two satellites with equal rest masses of 100 kg are traveling toward each other in deep space. They have identical speeds of 0.600c
The satellites collide and somehow manage to stick together. What is the rest mass of the combined object after the collision?
A) 200 kg
B) 225 kg
C) 250 kg
D) 275 kg
E) 300 kg
C
You might also like to view...
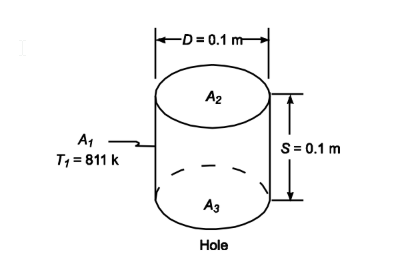
A large slab of steel 0.1-m-thick contains a 0.1-m-diameter circular hole, whose axis is normal to the surface. Considering the sides of the hole to be black, specify the rate of radiative heat loss from the hole. The plate is at 811 K, the surroundings are at 300 K.
GIVEN
• A large slab of steel with a hole whose axis is normal to the surface
• Slab thickness (S) = 0.1 m
• Hole diameter (D) = 0.1 m
• Plate temperature (T1) = 811 K
• Temperature of surrounding (T?) = 300 K
FIND
• The rate of radiative heat loss from the hole (qr)
ASSUMPTIONS
• The sides of the hole are black
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
What is the speed of light in a material that has an index of refraction of 2.0?
A. 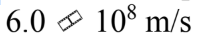
B. 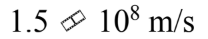
C. 
D. 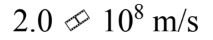
E. No such index can exist.
Which of the following is true of quasars?
A) They manifest very small redshifts. B) Their spectra are similar to stellar spectra. C) They represent the structure of galaxies as they are in the present time. D) Their luminosity is 10 to 1000 times the luminosity of a large galaxy.
In comparing first magnitude Deneb with second magnitude Polaris, we find that
A) Polaris is in reality much more luminous. B) Deneb must be much hotter than Polaris. C) Deneb appears 2.5 times brighter to us than does Polaris. D) Polaris is really 100 times brighter than nearby Deneb. E) Deneb is really much closer than Polaris.