What are the factors that contribute to productivity growth in the market economy and which of them is considered most important?
What will be an ideal response?
There are three oft-cited factors that contribute to productivity growth. The first is the education and experience of the labor force that enables workers to produce more and better goods in a given period of time. The second is investment in plant and equipment that gives workers more and better tools to do their work with. The third is innovation—the discovery and introduction of new production methods and new products that increase the productivity of workers. Innovation is considered the most important of these three factors. Competition between firms in terms of innovation is considered to be the main engine of growth in the market economy.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is true of marginal cost?
a. Marginal cost is the cost per unit of output produced. b. Marginal cost is the change in total cost divided by the change in total output. c. Marginal cost curve is negatively sloped at the profit-maximizing level of output. d. Marginal cost is equal to total cost divided by the quantity of output. e. Marginal cost initially increases with an increase in output but subsequently declines.
Which of the following statements is correct?
a. The demand for natural gas is more elastic over a short period of time than over a long period of time. b. The demand for smoke alarms is more elastic than the demand for Persian rugs. c. The demand for bourbon whiskey is more elastic than the demand for alcoholic beverages in general. d. All of the above are correct.
How did an increase in consumer confidence change the final equilibrium point of the expansionary policy as shown in this graph?
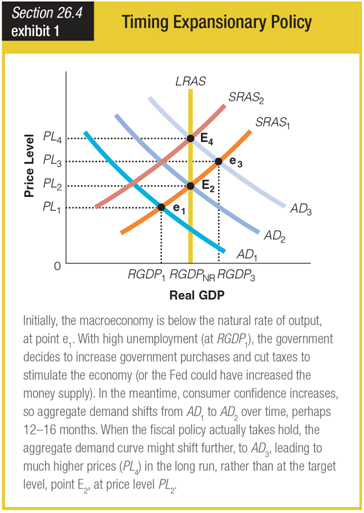
a. Instead of reaching the target of E3 and at RGDP3, the final result is E4 at RGDPNR.
b. Instead of reaching the target of E2 and at RGDPNR, the final result is E4 at RGDPNR.
c. Instead of reaching the target of E2 and at RGDPNR, the final result is E3 at RGDP3.
d. Instead of reaching the target of E3 and at RGDP3, the final result is E1 at RGDP1.
The marginal propensity to consume is
A. That part of the average consumer dollar that goes to saving. B. Always equal to 1. C. The change in consumption divided by the change in disposable income. D. The same as the spending multiplier.