From 1860 to 1910, U.S. mobility between social classes and occupations
(a) distracted immigrants.
(b) increased the potential migrant's opportunity cost of staying in Europe.
(c) attracted immigrants to the U.S.
(d) decreased foreign investment in the U.S.
(b)
You might also like to view...
Explain why public goods can be classified as market failure? Explain what problem arises when public goods are produced?
What will be an ideal response?
An externality is a situation in which
A) private costs diverge from social costs. B) internal costs diverge from private costs. C) there are no social costs. D) the cost borne by the consumer is greater than the monetary price.
According to the graph shown, if this economy is an autarky, its equilibrium price is:
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good, as well as a tariff and the world price for that good.
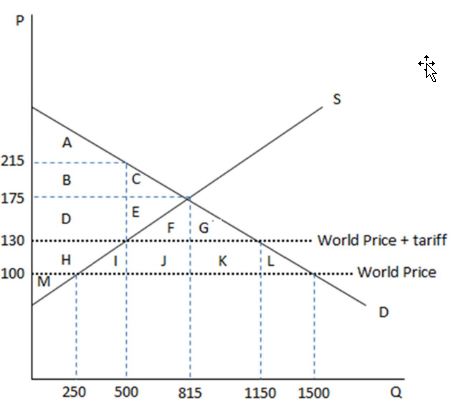
A. $175 at a quantity of 815.
B. $215 at a quantity of 500.
C. $130 at a quantity of 1150.
D. $130 at a quantity of 500.
Suppose that consumption spending is $4,200 billion, spending on durable goods is $1,200 billion, and spending on services is $2,000 billion. What does spending on nondurable goods equal?
A) $7,200 billion B) $1,000 billion C) $2,200 billion D) $3,200 billion E) There is not enough information to answer this question.