Refraction results from changes in light's
A) frequency.
B) incident angles.
C) speed.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
An 80-km/h airplane caught in a 60-km/h crosswind has a resultant speed of
A) 60 km/h. B) 80 km/h. C) 100 km/h. D) 141 km/h.
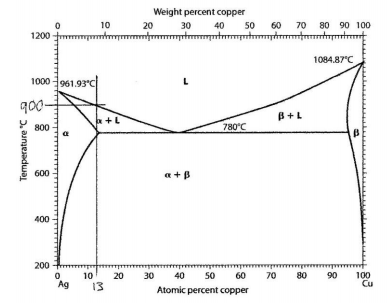
You want to produce a casting of sterling silver that is silver plus 13 atomic % copper. Pure silver is too soft for many applications, and adding 13 atomic % copper strengthens the silver without significantly changing the color. To produce the sterling silver casting, you are going to melt commercially pure silver and copper in a furnace, and then you will pour the liquid metal mixture into a mold. The following questions relate to this alloy.
(a) In selecting a furnace, what must be the minimum value of the high-temperature capability of your selected furnace?
(b) In transferring the liquid metal from the furnace to the mold, what is the minimum temperature that the metal can reach so that none of the metal has solidified?
(c) After the casting has cooled to room temperature, what phases are present, what is the equilibrium chemical composition (Ci) of each phase present, and what is the atom fraction (fi) of each phase present?
The _____ is an imaginary sphere of very large radius surrounding Earth to which the planets, stars, Sun, and Moon seem to be attached
A) galactic sphere B) celestial sphere C) equatorial sphere D) lunar sphere
A police crime lab is trying to determine whether someone was murdered or died as a result of an accident. He was struck in the temple by a 4.20 kg sculpture that is alleged to have fallen off a bookcase. The sculpture presumably fell a distance of 1.43 m and the corner that struck him had an area of 0.250 cm2 . If the time for the sculpture to stop was 1.00 ms, the pressure on his temple, in
N/m2, was a. 8.89 × 10^4. b. 1.65 × 10^5. c. 1.65 × 10^6. d. 8.89 × 10^8. e. 1.65 × 10^9.