Work: A person carries a 2.00-N pebble through the path shown in the figure, starting at point A and ending at point B. The total time from A to B is 6.75 min. How much work did gravity do on the rock between A and B?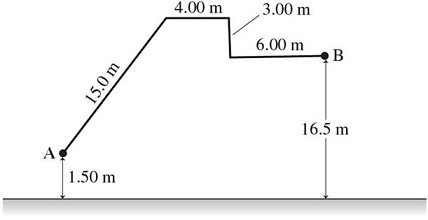
A. 30.0 J
B. -30.0 J
C. -56.0 J
D. 56.0 J
E. -36.0 J
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
A baseball leaves the bat with a speed of 47 m/s and an angle of 45° above the horizontal. A 5.0-m-high fence is located at a horizontal distance of 137 m from the point where the ball is struck. Assuming the ball leaves the bat 1.0 m above ground level, by how much does the ball clear the fence?
a. 59.7 m b. 47.7 m c. 49.7 m d. 121 m
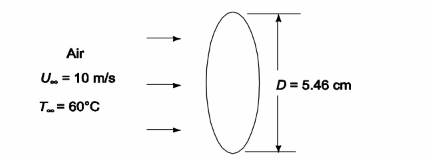
if the extrusion cross-section is elliptical with the major axis normal to the air flow and same mass per unit length. The major axis of the elliptical cross-section is 5.46 cm and its perimeter is 12.8 cm
GIVEN
• A long elliptical copper extrusion in an air stream
• Initial temperature (To) = 400°C
• Air Temperature (T?) = 50°C
• Air velocity (V?) = 10 m/s
• Surface emissivity (?) = 0.9
• Elliptical cross-section with major axis normal to the air flow
• Length of the major axis of the ellipse (D) = 5.46 cm = 0.0546 m
• Perimeter of ellipse (P) = 12.8 cm = 0.128 m
• Same mass per unit length as Problem 6.9
FIND
• The time (t) required for the center of the copper to cool to 100°C
ASSUMPTIONS
• Air flow is perpendicular to the axis of the extrusion
• Variation of the copper properties with temperature is negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the initial and final film temperature of 150°C
Thermal conductivity (ka) = 0.0339 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 29.6 × 10–69 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
Thermal conductivity (k) = 386 W/(m K) at 250°C Density (?) = 8933 kg/m3 at 20°C Specific heat (c) = 383 J/(kg K) at 20°C
The density of a _________ is greater than the density of a _________
a. white dwarf; neutron star b. neutron star; black hole c. pulsar; neutron star d. pulsar; white dwarf e. white dwarf; black hole
Energy Levels: The figure shows part of the energy level diagram of a certain atom. The energy spacing between levels 1 and 2 is twice that between 2 and 3. If an electron makes a transition from level 3 to level 2, the radiation of wavelength ? is emitted. What possible radiation wavelengths might be produced by other transitions between the three energy levels?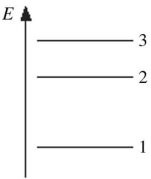
A. both ?/2 and ?/3 B. only ?/2 C. both 2? and 3? D. only 2?