In a closed economy, if Y remained the same, but G rose, T rose by the same amount as G, and C fell but by less than the increase in T, what would happen to private and national saving?
a. national saving would fall and private saving would rise
b. national saving would rise and private saving would fall
c. both national saving and private saving would fall
d. None of the above is correct.
c
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure above. If A forms a customs union with C, the value of trade diversion will be
A) $0. B) $10,000. C) $20,000. D) $40,000.
The currency component includes paper money and coins held in
A) bank vaults. B) ATMs. C) the hands of the nonbank public. D) the central bank.
Most of the world's economies are mixed economies because _________
a. a cartel of powerful transnational firms demands it. b. the market system of allocation is always best. c. the command system of allocation is always best. d. government intervention in an overall market system exists because markets fail when there is market power, a great deal of inequality, pollution externalities, or public goods.
Refer to Figure 8.6, which shows a firm's short-run average cost curves for three different levels of capital. Which of the following statements about short-run and long-run marginal cost is true?
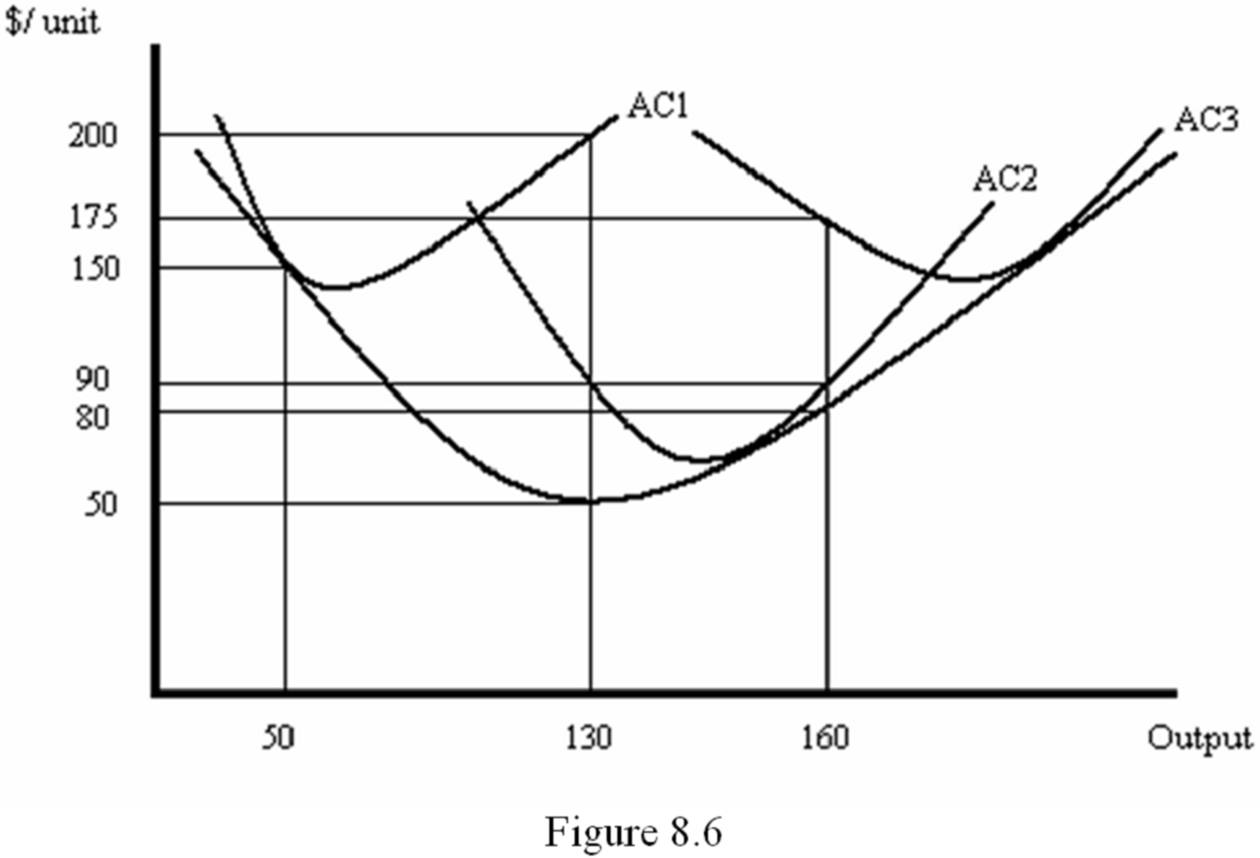
A. Long-run marginal cost equals short-run marginal cost at 50 units of output.
B. Long-run marginal cost equals short-run marginal cost at 130 units of output.
C. Long-run marginal cost equals short-run marginal cost at 160 units of output.
D. Long-run marginal cost and short-run marginal cost are never equal.