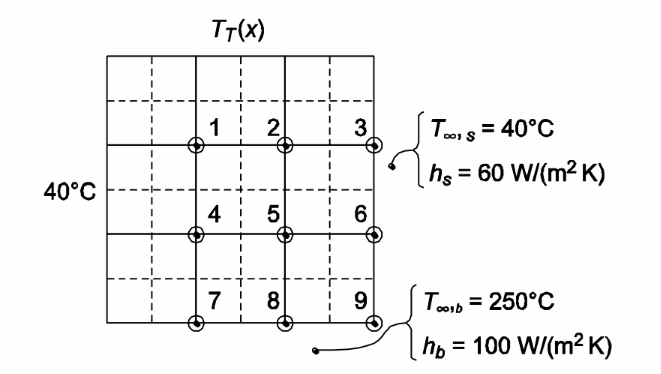
In a long, 30-cm square bar shown in the accompanying sketch, the left face is maintained at 40°C and the top face is maintained at 250°C. The right face is in contact with a fluid at 40°C through a heat transfer coefficient of 60 W/(m2 K) and the bottom face is in contact with a fluid at 250°C through a heat transfer coefficient of 100 W/(m2 K). If the thermal conductivity of the bar is 20 W/(mK), calculate the temperature at the 9 nodes shown in the sketch if the temperature distribution on the top surface of the bar varies sinusoidally from 40°C at the left edge to a maximum of 250°C in the center and back to 40°C at the right edge.
GIVEN
Square bar with one surface at fixed temperature, one surface with a specified temperature
distribution, and two surfaces with convective boundary conditions
FIND
(a) Temperature at 9 shown nodes
SKETCH
Define the following symbols

Since the temperature varies sinusoidally across the top surface we have
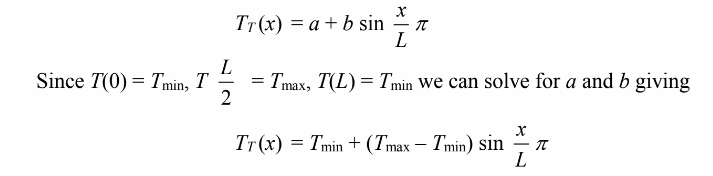
Now, define the temperature at the four nodes on the top edge as

the temperature at nodes 1, 2, 4, and 5 is just the average of the temperature at
the neighbor nodes
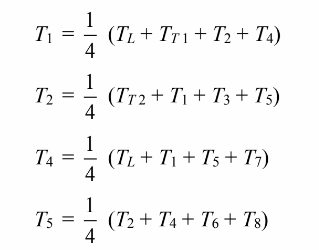
The remaining control volumes have convective boundary conditions and we need to develop
individual energy balance equations for each.
For the control volume surrounding node 3
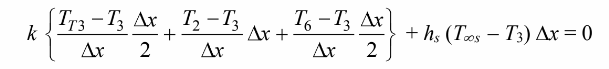
which can be solved for T3 as follows
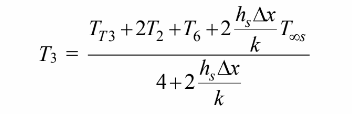
For the control volume at node 6
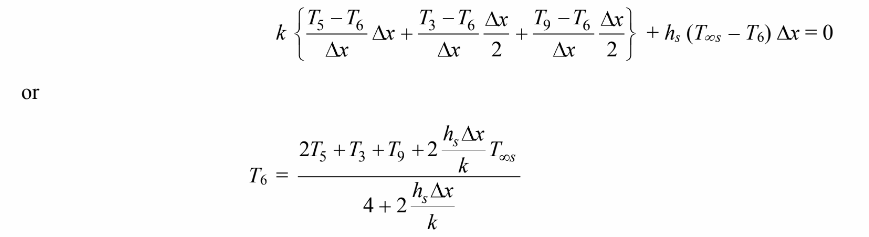
For the control volume at node 7
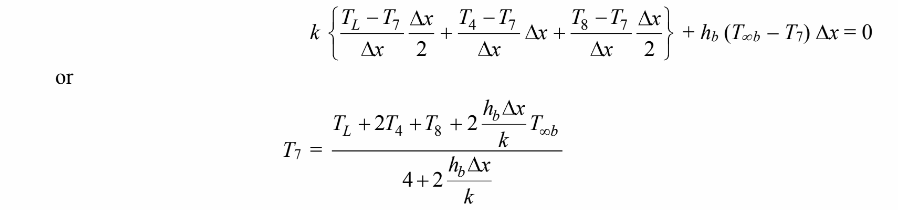
For the control volume at node 8
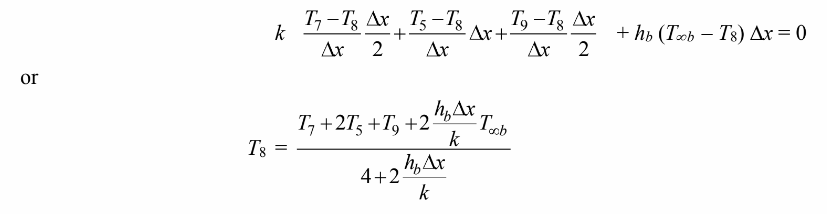
Finally, for the control volume at node 9
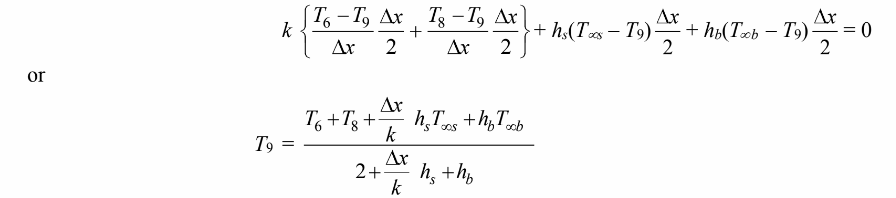
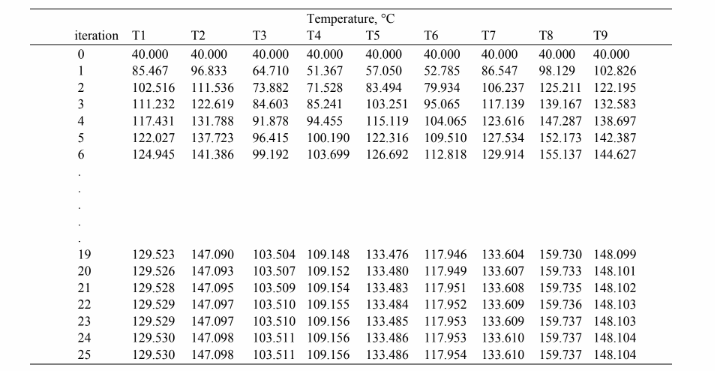
This set of equations can be solved iteratively. Here we used a spreadsheet to employ the Gauss-Seidel
iteration method. The table below shows the results of the first 25 iterations after which the calculation
appears to converge. Values for the 9 nodal temperatures at the zero iteration are the first guess.
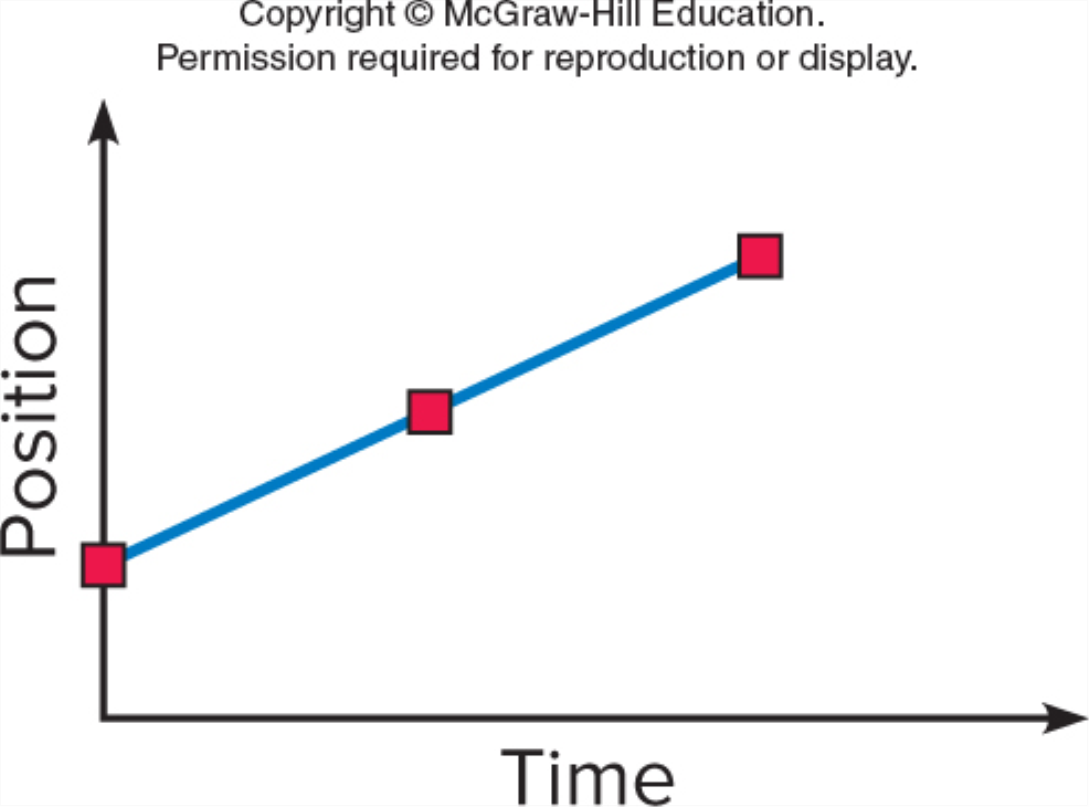
You might also like to view...
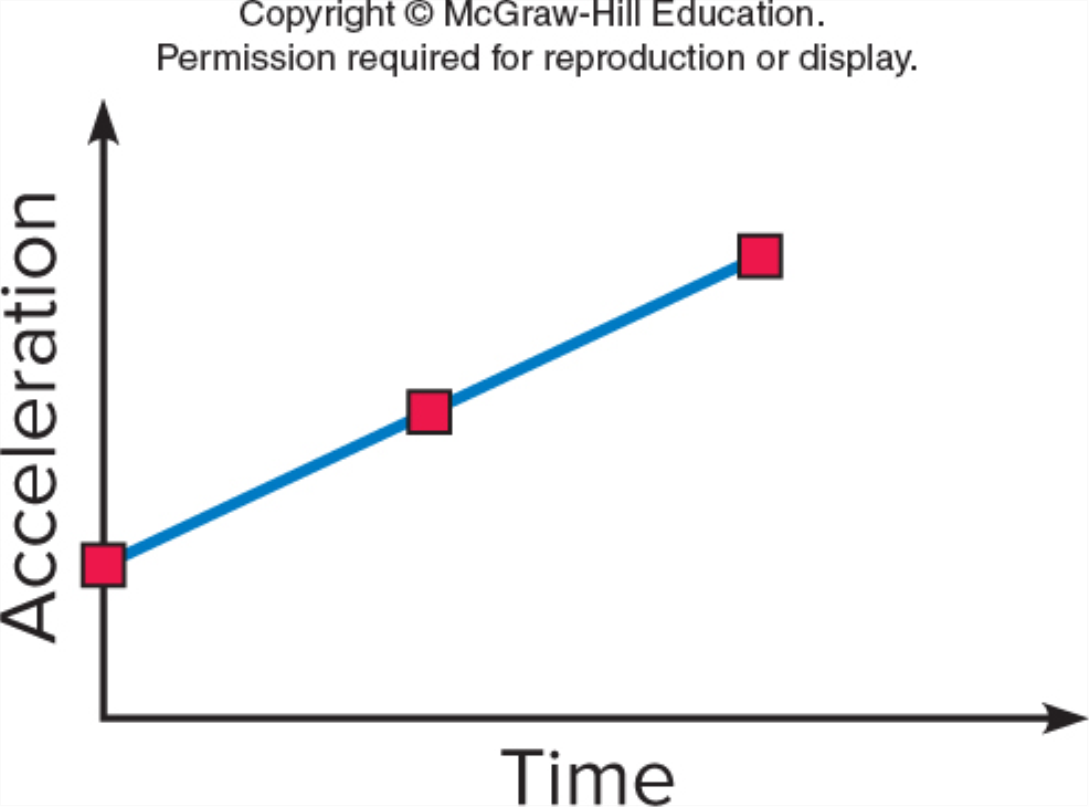
Which graph shows an object moving with a constant non-zero acceleration (note the vertical axes differ)?
GRAPH A
GRAPH B
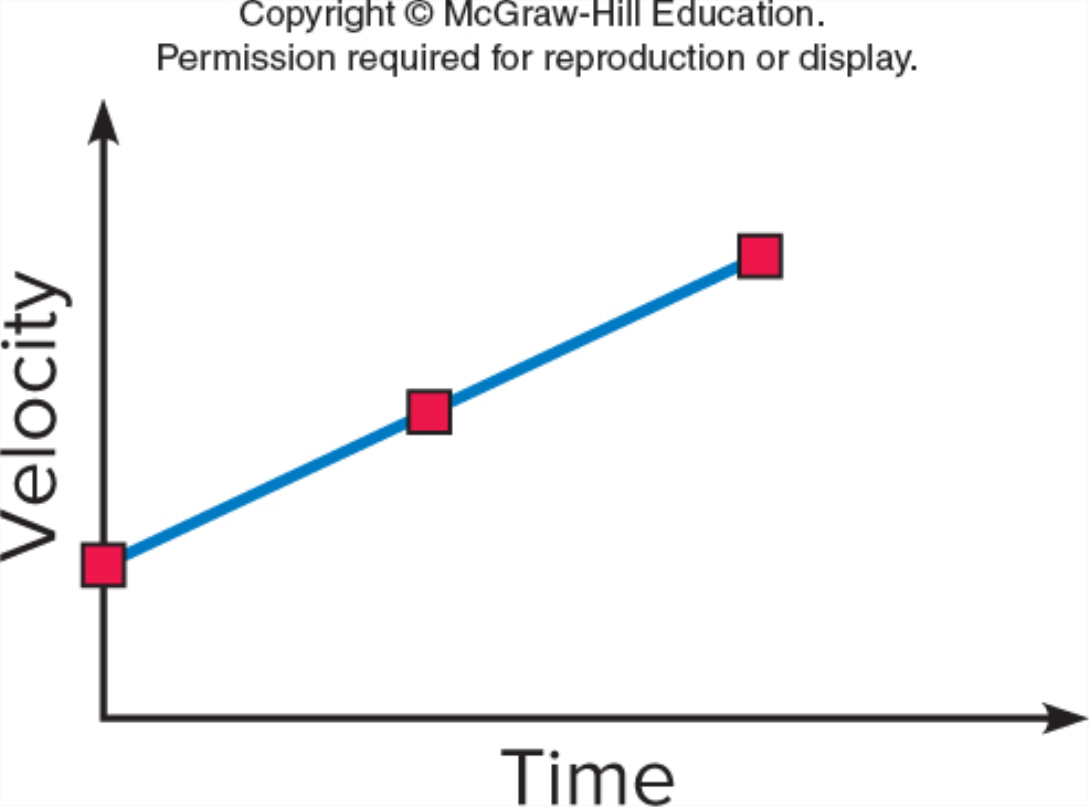
GRAPH C
In the HCl molecule, the bonding electrons spend
a. equal time around both atoms. b. all their time around only one of the atoms. c. more time around the H atom. d. more time around the Cl atom.
What is Fick’s law?
What will be an ideal response?
If the temperature changes by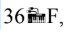 then what is the change in temperature in Celsius?
then what is the change in temperature in Celsius?
A. 40
B. 32
C. 26
D. 20
E. 15