According to the theory of liquidity preference, an increase in the price level causes the
a. interest rate and investment to rise.
b. interest rate and investment to fall.
c. interest rate to rise and investment to fall.
d. interest rate to fall and investment to rise.
c
You might also like to view...
Sailboats and motorboats share Emerson Lake, which nobody owns. The sailors say the motorboats are a hazard; the motorboaters say it is the other way around. Frequent collisions occur, with many injuries and some deaths every year. If the City of Emerson were to buy the lake itself,
a. the problem would be solved, because the lake would have an owner b. the problem would be solved, because no one could use the lake c. the city would still have to assign property rights so that use of the lake would be efficient d. the city would give the right to use the lake to the larger group e. the city would give the right to use the lake to the richer group
Assume that you know the following cost information about Fred's widget company: Its fixed cost is $9, and its total variable cost is $6 for 1 unit; $11 for 2; $ 15 for 3; 20 for 4; and 26 for 5 . Given the above information, a. the marginal cost of providing the second unit is $5. b. the total cost of producing 4 units is $29
c. the average total cost of producing five units is $7. d. all of the above are true.
If the government set a price ceiling at $8
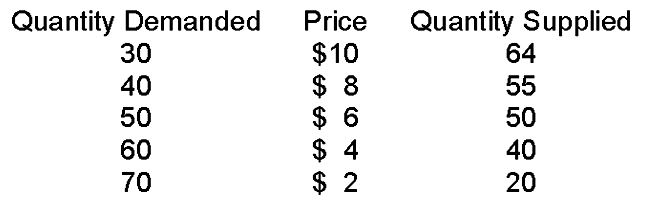
A. there would be a temporary surplus, then prices would fall to equilibrium.
B. there would be a permanent surplus, at least until the price floor was lifted.
C. the price would fall back to the equilibrium price.
D. the price floor would not have any effect on this market.
One of the conditions that must exist for the median-voter theorem to hold is:
A. candidates win by majority vote. B. voters may vote for a policy even if it not close to their own beliefs. C. there must be a run-off election in the event of a tie vote between two or more candidates. D. there is a simple in-favor/not-in-favor position held by each candidate.