Explain why despite enormous natural resources, much of Latin America's population remains in poverty and the region has been repeatedly experiencing financial crises
What will be an ideal response?
Most Latin America population remains in poverty because bad advise and inefficient proliferated about investment decisions having taken. At the same time, the revenues available to those able to exploit limited domestic markets inspired lobbying for imports licenses and expanding the market as well as corruption. Discrimination in the import that alternates financial system and poverty at the lowest income levels grew over time. Government corruption and bad administration of money have been one of the factors that enable Latin America population from growing. Since the 1950s and 1960s many of the Latin America countries in the region were able to attain amazing growth rates by exploiting the initially high returns from moving resources in to industrial uses from inefficient agricultural activities. Instead of using the growth to get rid of debts and decrease the deficit of the country, governments along with corrupt people wasted for getting about the debt that the country was facing.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 8-18. What is the GDP deflator in 2011 if 2016 is the base year?
A) 187 B) 87 C) 8.7 D) 0.87
Crowding out refers to the situation in which:
a. borrowing by the federal government raises interest rates and causes firms to invest less. b. foreigners sell their bonds and purchase U.S. goods and services. c. borrowing by the federal government causes state and local governments to lower their taxes. d. increased federal taxes to balance the budget causes interest rates to increase and consumer credit decreases.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 the result in the short run would be: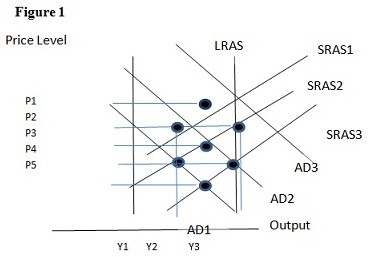
A. P1 and Y2. B. P3 and Y1. C. P2 and Y2. D. P2 and Y3.
The following graph shows average fixed costs, average variable costs, average total costs, and marginal costs of production.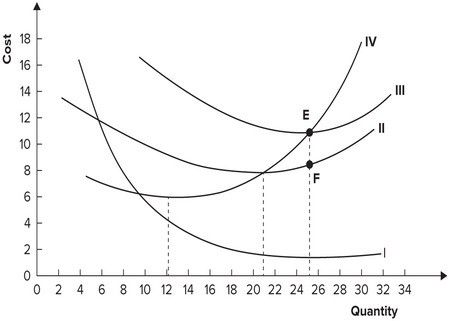 Average variable cost is minimized when output equals:
Average variable cost is minimized when output equals:
A. 21 units. B. 25 units. C. 12 units. D. 6 units.