In the principal-agent relationship, the principal is
A) the owner of a resource that has hired a third party to act in the best interest of that third party.
B) the person who is placed in control over resources that are not his own, with a contractual obligation to use these resources in the interests of some other party.
C) the person who is placed in control over resources that are not his own and agrees to compensate the resource owner in the event of outcomes that do not satisfy the resource owner.
D) the person who places his resources in professional hands in exchange for the professional's promise to act on the resource owner's behalf.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
In the term "Free Banking," the "free" means:
a. the freedom of any state legislature to charter a bank. b. the freedom of banks to mint U.S. coins. c. the freedom of anyone to start a bank. d. None of the above are correct.
A firm's marginal revenue is defined as:
a. the ratio of total revenue to total quantity produced. b. the additional output produced by lowering price. c. the additional revenue received due to technical innovation. d. the additional revenue received when selling one more unit of output.
Aluminum Aces dumps wastewater into a creek they have owned for decades. The new neighbor, Ms. Franklin, has tried to grow bamboo along the creek where it enters her property, but the wastewater kills about $1,000 worth of her bamboo each year. She offers Aluminum Aces $600 per year to add a new filter, which costs $400, to their system so wastewater will no longer kill her bamboo. Which of the following is true of this situation and necessary for it to fit the Coase theorem?
a. Neither party is worse off than before. b. Property rights are not defined. c. A positive externality is internalized. d. Transaction costs are high.
The table gives data on interest rates and investment demand (in billions of dollars) in a hypothetical economy.
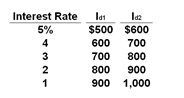
Refer to the above table. Assume that the public debt is used to expand the capital stock of the economy and that, as a consequence, the investment-demand schedule changes from Id1 to Id2. At the same time, the interest rate rises from 3% to 4% as the government borrows money to finance the public debt. How much crowding out of private investment will occur in this case?
A. $0
B. $100 billion
C. $600 billion
D. $700 billion