Explain the concepts of consumer surplus, producer surplus, and cooperative surplus
What will be an ideal response?
Consumer surplus refers to the maximum amount a buyer would be willing to pay for a good or service less the price he or she actually pays. Producer surplus refers to the amount a seller receives for a good or service beyond the minimum he or she would be willing to sell the good for. Cooperative surplus is the sum of all the net benefits received by the parties to a transaction, so it is the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
You might also like to view...
What happens to the demand for Xbox games if the price of an Xbox falls?
A) The demand for Xboxes decreases because the price of a substitute falls. B) The demand for Xboxes increases because the price of a complement falls. C) The demand for Xboxes decreases because the price of a complement falls. D) The demand for Xboxes remains unchanged.
In a study of whether prices are sticky or not, Alan Blinder supervised interviews of corporate executives on the frequency with which their firms change prices and found that
a. 55 percent of firms changed prices only once a year or less. b. over 20 percent of the firms changed prices more than 12 times per year. c. 10 percent of companies changed prices 4 to 12 times per year. d. there is not a considerable departure from auction-market behavior.
The poverty rate among female-headed households is around
A. 70%. B. 33%. C. 2%. D. 11%.
Refer to the figure below. This graph describes a good that: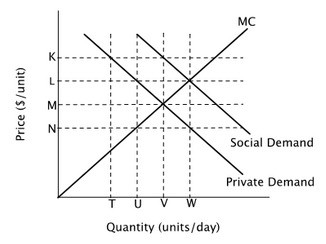
A. generates negative externalities. B. the government should tax. C. generates positive externalities. D. should be banned.