Any competitive equilibrium is Pareto-efficient because, with a competitive equilibrium,
A) the marginal rates of substitution are equal for all consumers.
B) the price line is the contract curve.
C) mutual gains from trade exist.
D) the slope of the price line equals the ratio of the MRS for all consumers.
A
You might also like to view...
In a market with positive externalities,
A) the efficient level of production is less than what competition will obtain. B) the efficient level of production is equal to what competition will obtain. C) the efficient level of production is more than what competition will obtain. D) there cannot be an efficient level of production.
Which of the following is true about the equation of exchange??
a) The equation of exchange can be presented as: M + V = P + Q. b) Velocity represents the average number of times that a dollar is used in purchasing final goods or services in a one-year period. c) ?If M decreases, and V increases, then P must rise and/or Q must rise. d) All of the above are true about the equation of exchange.
Exhibit 4-8 Demand and supply curves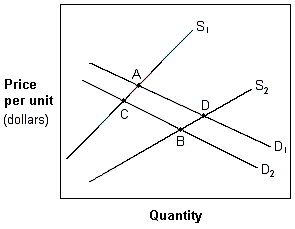
A. an increase in income and in the number of suppliers. B. an increase in the price of other goods. C. an increase in the population. D. a decrease in income if X is a normal good and an improvement in the technology used to produce the good.
In the national income accounts, the purchases of durables, nondurables, and services by households are classified as:
a) consumption. b) investment. c) net exports. d) government purchases.