A spacecraft (mass = m1) orbits a planet (mass = m2) in a circular orbit (radius = r). What is the minimum energy required to send this spacecraft to a distant point in space where the gravitational force on the spacecraft by the planet is negligible?
a. Gm1m2/(4r)
b. Gm1m2/R
c. Gm1m2/(2R)
d. Gm1m2/(3R)
e. 2Gm1m2/(5R)
c
You might also like to view...
A 2.00 m long horizontal uniform beam of mass 20.00 kg is supported by a wire as shown in the figure. The wire makes an angle of 20.00 degrees with the beam. Attached to the beam 1.400 m from the wall is a ball with a mass of 40.00 kg. What are the vertical and horizontal components of the force of the wall on the beam at the hinge?
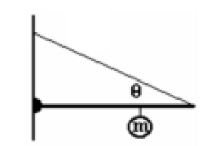
A. V = 175.6 N, H = 2,023 N
B. V = 186.6 N, H = 1,805 N
C. V = 195.4 N, H = 1,750 N
D. V = 200.6 N, H = 1,323 N
E. V = 215.6 N, H = 1,023 N
Which of the following objects never appears to exhibit retrograde motion in our sky?
A) The Sun B) Venus C) Mars D) Jupiter E) Saturn
The types of current carried by the headlights of an automobile, and by a plug-in toaster in your kitchen, are
A) both DC. B) both AC. C) AC and DC, respectively. D) DC and AC, respectively. E) None of the above.
Why aren't the three readings for background radiation in Procedure 1 identical?