What is genomic DNA–DNA hybridization MOST commonly used for?
a. comparing genomic GC content
b. distinguishing closely related genomes
c. genomic sequencing
d. multilocus sequence typing
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The 3-day test that is useful for identifying the rapid-growers, M. fortuitum and M. chelonae, and that measures the rate by which this enzyme breaks down phenolphthalein disulfate into phe-nolphthalein and other salts is the ____________ test
a. niacin. b. phenolphthalein. c. arylsulfatase. d. Tween 80.
The diagram illustrates two-hybrid screening. In which discipline would this technique be used?
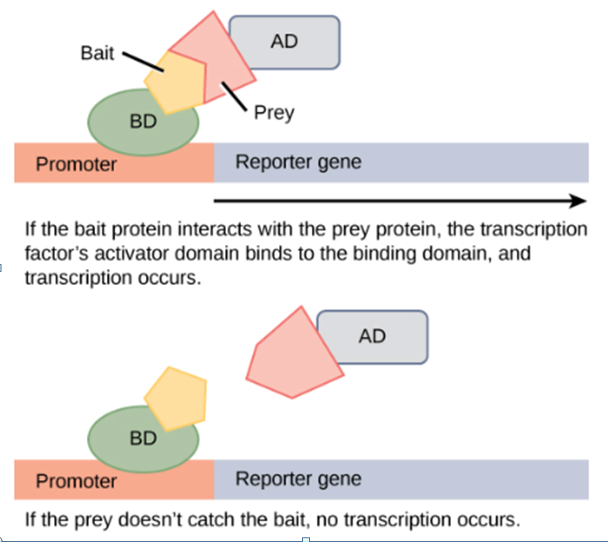
a. genomics
b. metabolomics
c. proteomics
d. bionomics
An organism that is made up of a fungus and an associated green alga or cyanobacterium is known as a
a. sac fungus. b. lichen. c. mycorrhizal root. d. club fungus.
During electron transport in photosynthesis, the inner compartment of the thylakoid membrane becomes:
A) filled with ATP. B) more acidic than the stroma. C) a storage site for electrons. D) a site for the synthesis of galactose molecules. E) a site for the synthesis of NADPH+.