Suppose a survey is taken concerning car safety. According to the survey, people strongly desire safer cars and indicate they are willing to pay substantially more for safer cars
Using this information, one auto firm adds numerous safety features to its car, raising the price by several thousand dollars. Sales drop sharply, and the firm loses profits. What went wrong?
The automaker was relying on what people say rather than on what they do. An economic model would have tried to predict whether the expected gains from driving safer cars would have been great enough for consumers to pay the higher price. Economic models are models of behavior and not models about how people think or whether people's views directly affect their actions. Also, they did not account for other factors
You might also like to view...
Disposable income is National income
A) less taxes collected from households and firms by the government. B) plus net taxes collected from households and firms by the government. C) less net taxes collected from firms by the government. D) less net taxes collected from households by the government. E) less net taxes collected from households and firms by the government.
Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct?
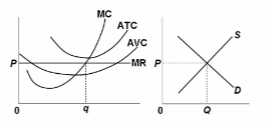
A. The diagrams portray neither long-run nor short-run equilibrium.
B. The diagrams portray both long-run and short-run equilibrium.
C. The diagrams portray short-run equilibrium but not long-run equilibrium.
D. The diagrams portray long-run equilibrium but not short-run equilibrium.
Calculate the annual percentage change in price level for the year 2014. Round to two decimal places.
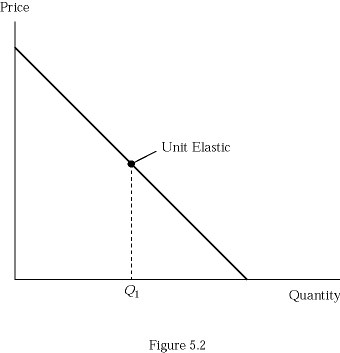 In Figure 5.2, at quantities larger than Q1,
In Figure 5.2, at quantities larger than Q1,
A. total revenue is rising. B. price elasticity is less than 1. C. price and total revenue are directly related. D. All of these