Which of the following is true of the price elasticity of demand of a product?
a. It measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded or quantity supplied to a change in one of the determinants of demand and/or supply.
b. It is calculated as the percentage change in the quantity demanded of the product divided by the percentage change in the price of the product.
c. It is calculated as the percentage change in the demand for the product divided by the percentage change in income of a consumer, everything else held constant.
d. It measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in the quantity supplied.
e. It is calculated as the percentage change in the quantity demanded of the product divided by the percentage change in the price of a related product, everything else held constant.
b
You might also like to view...
Economics seeks to use only positive analysis to
A) provide a value-free analysis. B) seek the best answer. C) predict how people should act. D) provide normative values.
A perfectly competitive firm will earn positive economic profits in the range of output for which the firm’s price is _________ its minimum average total cost.
A) below B) above C) equal to D) below its marginal cost and
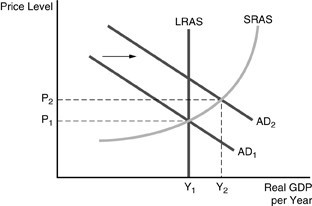 Refer to the above figure. Unexpected expansionary monetary policy has caused the aggregate demand curve to shift to AD2. In the long run
Refer to the above figure. Unexpected expansionary monetary policy has caused the aggregate demand curve to shift to AD2. In the long run
A. real GDP will be Y1, and the price level will be above P2. B. real GDP will be between Y1 and Y2, and the price level will be between P1 and P2. C. real GDP will be Y2, and the price level will be P2. D. real GDP will be Y1, and the price level will be P1.
Refer to the diagram of the market for product X. Curve S t embodies all costs (including externalities) and D t embodies all benefits (including externalities) associated with the production and consumption of X. Assuming the equilibrium output is Q 2 ,
we can conclude that the existence of external:
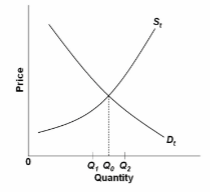
A. costs has resulted in an overallocation of resources to X.
B. benefits has resulted in an overallocation of resources to X.
C. costs has resulted in an underallocation of resources to X.
D. benefits has resulted in an underallocation of resources to X.