Consider a beam of free particles that each have a certain (nonrelativistic) kinetic energy K. If we double this kinetic energy, what happens to the beam’s wavelength?
A. It increases by a factor of 2.
B. It increases by a factor of 21/2.
C. It remains the same.
D. It decreases by a factor of 21/2.
E. It decreases by a factor of 2.
D. It decreases by a factor of 21/2.
You might also like to view...
The value of the momentum of a system is the same at a later time as at an earlier time if there are no
A. collisions between particles within the system. B. inelastic collisions between particles within the system. C. changes of momentum of individual particles within the system. D. internal forces acting between particles within the system. E. external forces acting on particles of the system.
Earth satellites are typically more than 100-km high so as to mainly be above the Earth's
A) atmosphere. B) gravitational influence. C) both of these D) none of the above
A radiating body originally has a Kelvin temperature To, and its surroundings are at 500K (To > 500K). If the Kelvin temperature of the radiating body is increased to 3To,
the net rate at which the body radiates increases by a factor of 333. What was the original temperature To?
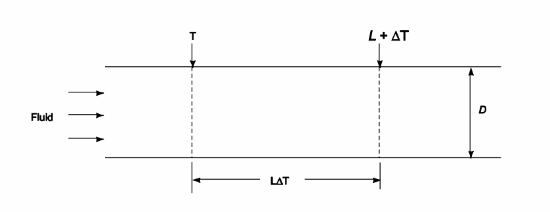
For fully turbulent flow in a long tube of diameter D, develop a relation between the ratio (L/?T)/D in terms of flow and heat transfer parameters, where L/?T is the tube length required to raise the bulk temperature of the fluid by ?T for fluids with Prandtl number of the order of unity or larger for liquid metals.
GIVEN
Fully developed turbulent flow in a long tube
Diameter = D
L/? T = Tube length required to raise the bulk temperature by ? T
FIND
A relationship for (L/?T)/D in terms of flow and heat transfer parameters using
(a) Equation 7.61 for fluids with Pr = 1
(b) liquid metals
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Constant fluid properties
Uniform wall temperatures
SKETCH