Why does the marginal resource cost exceed the wage rate in the case of a monopolistic firm? Explain and illustrate with an example
What will be an ideal response?
The monopolist is a large employer of a particular type of labor. As the monopolist seeks to obtain more workers, the monopolist must raise the wage rate for all workers, or else labor morale will deteriorate. When the increased wage rate is paid to all workers, the marginal resource cost will diverge from the wage rate because those hired previously at lower wage rates must now be compensated at the new hire wage rate, and this amount makes the marginal cost of hiring a new worker more than the wage rate for that worker.
For example, if the first worker hired by a firm was paid $6 an hour, then the marginal resource cost of the first worker would be $6. If the next worker that was hired required a $7 wage to become employed, then the second worker would cost $7 an hour; however, another $1 an hour would have to be paid to the first worker. Thus the marginal resource cost of the second worker would be $8 an hour instead of just $7. The wage rate and marginal resource cost diverge as the second worker is hired by the monopolist.
You might also like to view...
The euro is said to be selling at a ________ if the spot dollar price is $1.18 and the nine-month forward rate is $1.16
A) forward discount B) forward premium C) forward spread D) none of the above
The firm maximizes economic profit by finding the rate of output at which total revenue ________ total cost ________
a. equals; all else constant b. plus; equals c. minus; equals zero d. exceeds; by the greatest amount.
A mandatory seatbelt law ends up raising the number of traffic fatalities if it lowers fatalities per accident from 0.11 to 0.08 while raising the number of accidents per period from 100,000 to any more than
A) 108,000. B) 111,111. C) 137,500. D) 110,000.
Refer to the diagram, which is a rectangular hyperbola, that is, a curve such that each rectangle drawn from any point on the curve will be of identical area. In comparing the price elasticity and the slope of this demand curve, we can conclude that the:
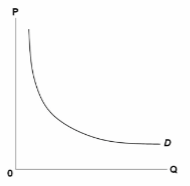
A. slope of a demand curve measures its elasticity.
B. elasticity of a demand curve measures its slope.
C. slope and elasticity of the curve are both constant throughout.
D. slope of the curve varies, but its elasticity is constant.