If the maximum E-component of an electromagnetic wave is 600 V/m, what is the maximum B-component?
a. 1.4 T
b. 1.8 × 10^?5 T
c. 2.0 × 10^?6 T
d. 1.0 × 10^?3 T
e. 1.6 × 10^?10 T
c
You might also like to view...
In a neutron star, the core is:
A) made of compressed neutrons in contact with each other. B) electrons and protons packed so tightly they are in contact. C) constantly expanding and contracting. D) primarily iron and silicon. E) no longer rotating.
Discuss advantages and disadvantages of two methods for solving one-dimensional steady conduction problems.
What will be an ideal response?
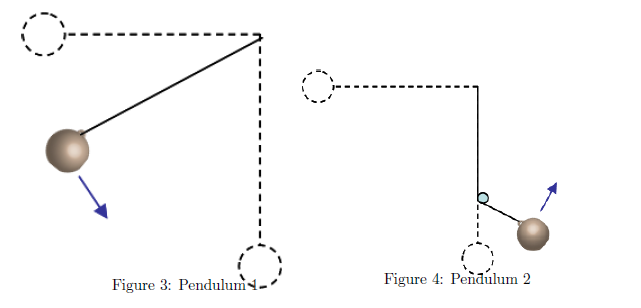
A mass m = 4.7 kg hangs on the end of a massless rope L = 2.05 m long. The pendulum is held horizontal and released from rest.
1) How fast is the mass moving at the bottom of its path?
2) What is the magnitude of the tension in the string at the bottom of the path?
3) If the maximum tension the string can take without breaking is Tmax = 382N, what is the maximum mass that can be used (Assuming that the mass is still released from the horizontal and swings down to its lowest point.)
4) Now a peg is placed 4/5 of the way down the pendulum's path so that when the mass falls to its vertical position it hits and wraps around the peg. As it wraps around the peg and attains its maximum height it ends a distance of 3/5 L below its starting point (or 2/5 L from its lowest point). How fast is the mass moving at the top of its new path (directly above the peg)?
5) Using the original mass of m = 4.7 kg, what is the magnitude of the tension in the string at the top of the new path (directly above the peg)?
What types of fundamental particles are in an atom?
A) just up quarks and top quarks B) just neutrons and electrons C) just down quarks, electrons, and positrons D) just up quarks, down quarks, and electrons E) just electons and positrons