A bowed-outward production possibilities curve demonstrates the concept of
A. increasing opportunity costs at first but the opportunity costs steadily decrease as you move down along the curve.
B. increasing opportunity costs as production shifts from the production of one good to the production of the other good.
C. constant opportunity costs as production shifts from the production of one good to the production of the other good.
D. decreasing opportunity costs as production shifts from the production of one good to the production of the other good.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
There are two players in a game. At each round of the game, one player has to trust the other for a particular task. In the first round, Player 1 has to decide whether he will trust Player 2
If he does not trust Player 2, he will get one-third of the prize money, while Player 2 will get the rest of the prize money. If he trusts Player 2, Player 2 can either cooperate with him or defect. If Player 2 defects, Player 1 will earn $0, while Player 2 will get the entire prize money. If Player 2 cooperates, each of them will get half the prize money. What will the equilibrium outcome of this game be if Player 1 can impose a guilt penalty of two-thirds of the prize money and is known to be a vengeful player?
Over the years most monetary policy experts would agree with each of the following statements, except:
A. the reserve requirement is not useful as an operational instrument. B. central bank lending is necessary to ensure financial stability. C. transparency in policy making hinders accountability. D. short-term interest rates are the best tool to use to stabilize short-term fluctuations in prices and output.
According to supply-side economics, changes in marginal tax rates will have which of the following effects?
A) change the incentive to work
B) change the incentive to save
C) change the incentive to invest
D) all of the above
Refer to the following graph.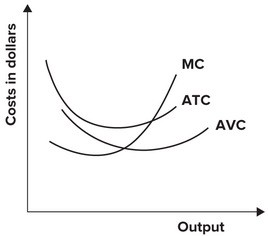 This set of cost curves is:
This set of cost curves is:
A. wrong because the marginal cost curve does not intersect the average total cost curve. B. wrong because the average variable and average total cost curves are switched. C. correct. D. wrong because the marginal cost curve should go through the minimum points of the AVC and ATC curves.