In which of the following cases does TANSTAAFL apply?
a. common use of land for grazing of sheep
b. use of air in industrial processes
c. use of water for power plant cooling
d. TANSTAAFL applies in all the above cases.
e. TANSTAAFL does not apply in any of the above cases.
D
You might also like to view...
A thin ribbon of a silver alloy 2.00-cm wide and 0.0150-mm thick carries a current of 6.98 A perpendicular to a magnetic field. The Hall voltage is found to be 1.24 × 10?4 V when the magnetic field is 2.50 T. Calculate n, the number of charge carriers per cubic meter.
What will be an ideal response?
What does the Sherwood number represent?
What will be an ideal response?
A light oil flows through a copper tube of 2.6-cm-ID and 3.2-cm-OD. Air flows perpendicular over the exterior of the tube as shown in the following sketch. The convection heat transfer coefficient for the oil is 120 W/(m2 K) and for the air is 35 W/(m2 K). Calculate the overall heat transfer coefficient based on the outside area of the tube (a) considering the thermal resistance of the tube, (b) neglecting the resistance of the tube.
GIVEN
• Air flow over a copper tube with oil flow within the tube
• Tube diameters
? Inside (Di) = 2.6 cm = 0.026 m
? Outside (Do) = 3.2 cm = 0.032 m
• Convective heat transfer coefficients
? Oil h i= 120 W/(m2 K)
? Air h o= 35 W/(m2 K)
FIND
• The overall heat transfer coefficient based on the outside tube area (Uo), (a) considering the thermal resistance of the tube, and (b) neglecting the tube resistance
ASSUMPTIONS
• Uniform heat transfer coefficients
• Variation of thermal properties is negligible
SKETCH
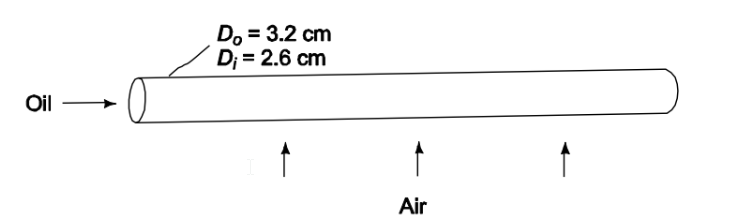
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the thermal conductivity of copper (k) = 392 W/(m K) (at 127°C)
The ionic charge of the nitrite ion in Al(NO2)3, aluminum nitrite, must be
a. 3+. b. 1–. c. 3–. d. 1+.