Given the graph, the quantity that would be associated with the price of $1 in a demand table would be: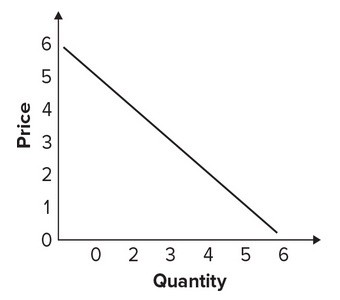
A. 6.
B. 5.
C. 4.
D. 3.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Country X experiences an increase in Real GDP and an increase in per-capita Real GDP. It follows that
A) the residents of country X are happier than they used to be. B) the benefits of economic growth outweigh the costs of economic growth. C) the costs of economic growth outweigh the benefits of economic growth. D) all the residents of country X are "richer" in terms of goods and services than they used to be. E) none of the above
Economist A believes that the case for government is a strong one, but she doesn't always say, when it comes to negative externalities, that government can turn an inefficient market outcome into an efficient outcome. Which statement is economist A most likely to make?
A) If the tax placed on the activity that generates the negative externality is too large, we are not likely too move from inefficiency to efficiency. B) If the subsidy placed on the activity that generates the negative externality is too small, we are not likely to move from inefficiency to efficiency. C) If there is a free rider problem, then government cannot solve the problem of negative externalities. D) a and b E) none of the above
An investor puts $1,000 into an investment that will return $1,250 one-half of the time and $900 the remainder of the time. The expected return for this investor is:
A. $1,075 B. 15.0% C. 5.0% D. 7.5%
Suppose that a regulatory agency has imposed marginal cost pricing on a natural monopolist. We expect that
A. the firm will rise its price above marginal cost. B. the firm will earn only a normal profit. C. the firm will earn economic losses. D. the firm's average total cost of production is rising over the relevant range of production.