What is the real GDP after four years if Country A's average annual growth rate is 8.6 percent and the initial real GDP was $2,756.0 million?
A. $3,833.5 million
B. $3,250.4 million
C. $2,993.0 million
D. $1,077.5 million
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Assume that business investment spending rises, and the increase is funded by greater borrowing in the capital markets. If the nation has low mobility international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the GDP Price Index and the nominal value of the domestic currency in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? a. The GDP Price Index rises and nominal value of the
domestic currency falls. b. The GDP Price Index falls and nominal value of the domestic currency rises. c. The GDP Price Index rises and nominal value of the domestic currency remains the same. d. The GDP Price Index rises and nominal value of the domestic currency rises. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
The CPI is more commonly used as a gauge of inflation than the GDP deflator is because
a. the CPI is easier to measure. b. the CPI is calculated more often than the GDP deflator is. c. the CPI better reflects the goods and services bought by consumers. d. the GDP deflator cannot be used to gauge inflation.
Suppose country X currently does not produce widgets. Instead, it imports widgets from country Z. Then country X establishes a preferential trading agreement with country Y. Following the formation of the PTA, it imports widgets from country Y. What has occurred?
a. There is trade diversion and a welfare loss for country X. b. There is trade creation and a welfare loss for country Y. c. There is trade diversion and a welfare gain for country X. d. There is trade creation and a welfare gain for country Y.
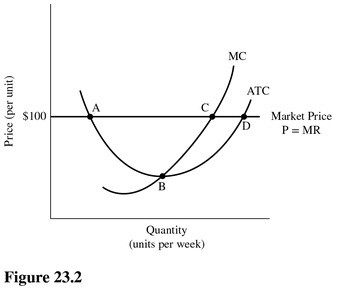 Refer to Figure 23.2 for a perfectly competitive firm. This firm will maximize profits by producing the level of output that corresponds to point
Refer to Figure 23.2 for a perfectly competitive firm. This firm will maximize profits by producing the level of output that corresponds to point
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.