If a material cannot transfer charge along its length, the material is:
a. a metal.
b. a conductor.
c. an insulator.
d. self-contained.
e. a magnet.
c
You might also like to view...
The absolute magnitude of a star is the apparent magnitude it would have if it were 10 pc from Earth
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
A multi-tube heat exchanger is used in a process plant to pre-heat air before it enters a combustion chamber, using low pressure steam that flows inside the tubes and condenses. The tube bundle is configured with 6-cm outer diameter tubes in a staggered arrangement as shown in the accompanying figure. The condensing steam in the tubes maintains their outer surface temperature at 117°C, and air at 60° flows across the tube bank with a free stream velocity of 1.0 m/s. Determine the average heat transfer coefficient for air.
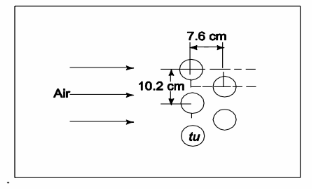
GIVEN
• Air flow through the tube bank shown
• Air temperature (Ta) = 60°C
• Air velocity (Us) = 1 m/s
• Tube outside diameter (D) = 6 cm = 0.06 m
• Tube wall temperature (Tw) = 117°C FIND
• The average heat transfer coefficient ( ch ) ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0279 W/(m
K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 19.4 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 At Tw: Prs = 0.71
A driver in a 1000 kg car traveling at 20 m/s slams on the brakes and skids to a stop. If the coefficient of friction between the tires and the horizontal road is 0.80, how long will the skid marks be?
A) 26 m B) 21 m C) 33 m D) 24 m
When a neutron and proton combine to form a deuteron, a 2.2 million electron volt gamma ray is emitted. What does this indicate about the binding energy of the deuterium nucleus?
a. Its binding energy is negative, i.e., it is unstable. b. It has a small binding energy. c. Its binding energy is about 2.2 million electron volts. d. The deuterium nucleus is slightly more massive than the sum of the proton and neutron masses, because of energy mass equivalence. e. The deuterium nucleus contains 2.2 million electron volts more energy than the separated neutron and proton.