The theory of purchasing-power parity primarily explains
a. why trade deficits tend to move to zero over time.
b. how foreign prices affect domestic prices.
c. the determination of the real exchange rate.
d. why a change in the real exchange rate changes a country's net exports.
c
You might also like to view...
The process in which economic growth destabilizes existing regimes and reduces the political power of rulers and monarchs is referred to as:
A) institutional destruction. B) polarization. C) division of powers. D) political creative destruction.
An increase in the quantity demanded of a good is most often due to
a. current prices b. higher prices c. higher income d. lower prices e. technological change
In the short run, a firm considers its fixed cost as a(n):
A. sunk cost. B. variable cost. C. implicit cost. D. marginal cost.
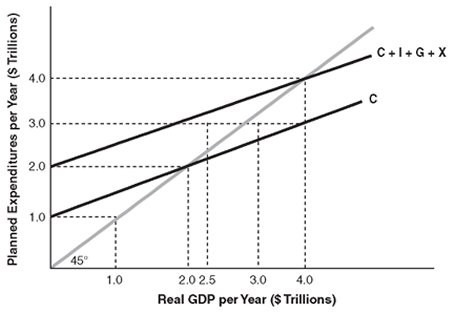 In the above figure, at the equilibrium level of real GDP, there is
In the above figure, at the equilibrium level of real GDP, there is
A. a negative tax rate. B. zero saving. C. negative saving. D. positive saving.