Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. The Keynesian analysis assumes that ample resources will be available to increase production if planned investment increases when the economy is at less than full employment.
2. The Keynesian analysis differs from classical analysis in its short-run analysis of the economy.
3. The monetarist school is primarily concerned with unemployment and recessions.
4. The monetarist school is more similar to the Keynesian school than the classical school.
5. The time lags lead monetarists to contend that monetary policy is counterproductive.
6. The new classical school holds that rational expectations tend to defeat the goals of monetary policy.
7. The new classical school contends that government fiscal policy is better than monetary policy in controlling inflation.
1. TRUE
2. TRUE
3. FALSE
4. FALSE
5. TRUE
6. TRUE
7. FALSE
You might also like to view...
Christy's Haircuts, the sole supplier of haircuts in a small town, faces the demand schedule shown in the table above. What is Christy's marginal revenue from the 25th haircut?
A) zero B) $5.00 C) $17.50 D) $50.00
The late Hugo Chavez, Venezuela's former president, proposed that the independence of the Venezuelan central bank be eliminated
Given the research on the relationship between central bank independence and inflation, we should expect this event to cause inflation to ________ and the real exchange rate to ________ between the two counties. (Assume the nominal exchange does not change, and that the United States is the domestic country). A) rise in Venezuela relative to the United States; fall B) rise in Venezuela relative to the United States; rise C) fall in Venezuela relative to the United States; fall D) fall in Venezuela relative to the United States; rise
The long-run average total cost curve of a firm envelops many short-run average total cost curves
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Exhibit 4-3 Supply and demand curves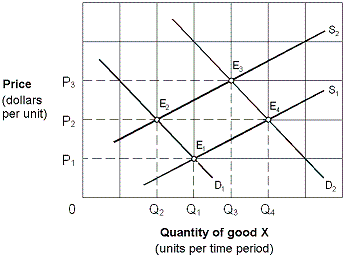
A. E1. B. E2. C. E3. D. E4.