Medigap policies are designed to offer:
a. coverage for Part D out-of-pocket spending.
b. catastrophic coverage for costs that exceed traditional Medicare's out-of-pocket maximum.
c. long-term care coverage for the elderly.
d. coverage for dental and vision care.
e. first dollar coverage for out-of-pocket spending on deductibles and coinsurance.
e. first dollar coverage for out-of-pocket spending on deductibles and coinsurance
You might also like to view...
The above figure illustrates a perfectly competitive wheat farmer
a. What will be the firm's profit-maximizing price and output? b. When the farmer produces 25,000 bushels of wheat, the difference between the firm's average total cost and the price is at its maximum. Explain why this amount of wheat either is or is not the profit-maximizing quantity.
Table 36-1Suppose the economy of Macroland is described by the following:C = 200 + 0.8 DI (DI = disposable income)I = 300 + 0.2Y?50r (Y = GDP)(r, the interest rate, is measured in percentage points. For example, a 9 percent interest rate is r = 9).For this economy, assume that the Federal Reserve uses its monetary policy to peg the interest rate atr = 5G = 750T = 0.25YX = 200M = 150 + 0.2YHint: DI = Y?T From Table 36-1, compute equilibrium GDP for Macroland.
A. 3,000 B. 2,950 C. 2,625 D. 2,525
If the population of a country is 1,000,000 people, its labor force consists of 600,000, and 60,000 people are unemployed, the unemployment rate is:
A. 6.0 percent. B. 6.6 percent. C. 10.0 percent. D. 60.0 percent.
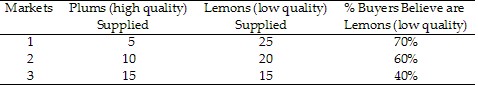
 In Table 9.3, Market 3 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed lemons account for:
In Table 9.3, Market 3 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed lemons account for:
A. 45% of the market. B. 50% of the market. C. 55% of the market. D. 60% of the market.