Where would you see Polaris, the north star?
What will be an ideal response?
On the northern horizon.
You might also like to view...
Compare the rate of condensate flow from the pipe in Problem 8.28 (air pressure = 200 kPa) with that for a 3.89-cm-OD pipe and 200 kPa air pressure. What is the rate of condensate flow if the 2 cm pipe is submerged in a 20°C constant-temperature water bath?
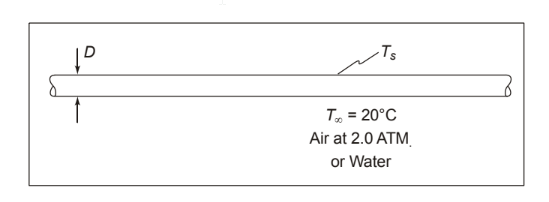
GIVEN
• A long horizontal copper pipe carrying saturated steam within an environmental testing chamber or a water bath
• Steam pressure = 120 kPa
• Ambient pressure (P) = 2 atm
• Ambient air or water temperature (T?) = 20°C
FIND
Rate of condensate flow for
(a) Diameter (D) = 3.89 cm = 0.0389 m Fluid is air at 2.0 atm
(b) Diameter (D) = 2 cm = 0.02 m Fluid is water at T? = 20°C
ASSUMPTIONS
• Pressure change has no effect on absolute viscosity, thermal conductivity, or specific heat of the air
• Air is still
• Convective thermal resistance on the inside of the pipe is negligible
• Thermal resistance of the copper pipe is negligible
• The air behaves as an ideal gas
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
For saturated steam at 0.12 MPa, the heat of vaporization (hfg) = 2238 kJ/kg, and the temperature (Ts) = 105°C.
for dry air at the mean temperature of 62.5°C and one atmosphere
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00298 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0281 W/(m K)
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 at P = 2.0 Atm,
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 9.83 × 10–6 Ns/m2
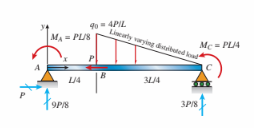
The simply supported beam ABC shown below is acted upon by applied axial force P at B; by linearly varying distributed load q on BC; and by applied moments MA and MC. Reaction forces are given in the figure in terms of load variable P. The axial force (N), shear (V), and bending moment (M) at mid-span are (in terms of variables L and P):
(A) 0, 0.22P, 0.63PL
(B) P, 0.29P, 0.33PL
(C) 0, 1.36P, 0.33PL
(D) 0, 0.29P, 0.33PL
What is the maximum number of 60-W light bulbs you can connect in parallel in a 100-V home circuit without tripping the 30-A circuit breaker?
a. 18 b. 24 c. 49 d. 36 e. 56
9.0 g of water in a 2.0-L pressure vessel is heated to 300°C. What is the pressure inside the container? (R = 0.082 L • atm/mol • K, one mole of water has a mass of 18 grams)
a. 12 atm c. 24 atm b. 16 atm d. 32 atm