An animal found in the rocky intertidal zone has eight overlapping plates and is tightly adhering to the rock with a
muscular foot. This animal is most likely a member of the class:a.
Polyplacophora.
b. Cephalopoda.
c. Polychaeta.
d. Gastropoda.
e. Bivalvia.
a
You might also like to view...
Which of these biomes has a plant composition that is most similar to the temperate coniferous forest?
A. alpine B. taiga C. deciduous forest D. rain forest E. chaparral
Which of the following pairs are NOT homologous?
A. the wing of a bat and the front flipper of a whale B. the wing of a bat and the wing of a chicken C. the foreleg of a turtle and the front flipper of a whale D. the wing of an insect and the wing of chicken E. both the wing of an insect and chicken and the wing of a bat and chicken
What nucleotide change is a shared derived character for species A, B, and C, but not for species G?
Note: A,T,G, and C refer to nucleotide bases, and the numbers refer to the position of the base in the nucleotide sequences. For example, A6 refers to an adenine at the sixth position.
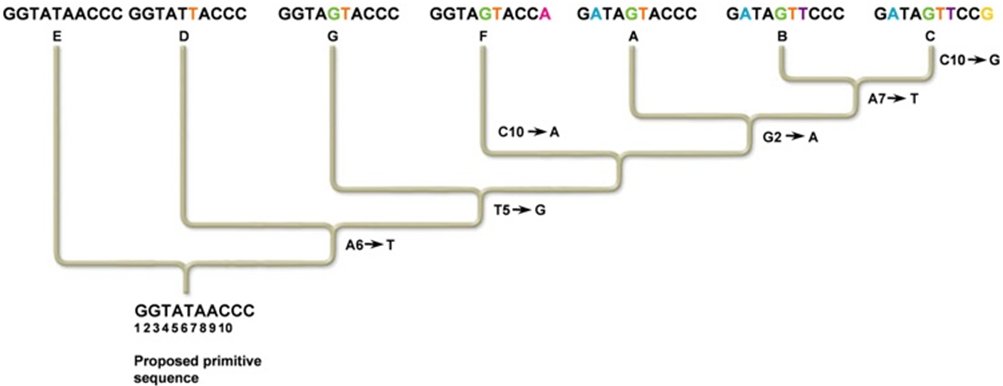
A. Changing the second G to an A is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
B. Changing the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
C. Changing the second G to a T is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
D. Changing the second G to an A and the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
E. None of these show a change in derived characteristics for A, B, and C that are not found in G.
What is a possible mechanism resulting in the displayed relationship between a fe-male's capture by a predator while mating and the body size of the male she is mating with?
Explain the overall trend and ignore the s-shaped fluctuation at intermediate body sizes for the purpose of this question. a. Large females tend to mate with large males, and large females are less likely to be caught. b. Large mating partners slow females down and make them easy prey. c. While mating with a large male the couple becomes a less attractive prey item. d. Copulations with large males are shorter than copulations with small males, thereby decreasing the time during which females are less mobile. e. A, C, and D.