An example of someone who irrationally considers sunk costs when making a decision is most likely:
A. a family that pays $20 to enter a state park for the day and leaves after an hour.
B. a family that pays $20 to enter a state park for the day and stays all day.
C. someone who paid $50 for a ticket to a baseball game and ends up sitting through the entire game in the freezing rain without a jacket.
D. someone who paid $50 for a ticket to a baseball game and ends up sitting through the entire game enjoying himself.
C. someone who paid $50 for a ticket to a baseball game and ends up sitting through the entire game in the freezing rain without a jacket.
You might also like to view...
When private property rights in a country are not secure, people cannot use their property as collateral for loans
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
When the exchange rate for a currency rises so that the currency trades for more of other currencies, it is said to be depreciating
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Government spending as a percent of national income
A) peaked during the Reagan administration. B) peaked during World War II. C) has been steadily climbing since 1850. D) has been almost constant this century.
Refer to the graphs below. In Graph B, assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at point x1 but then there is an increase in the price level from P1 to P2. In the long run, this change will lead to:
In the graphs below, QP refers to the economy's potential output level.
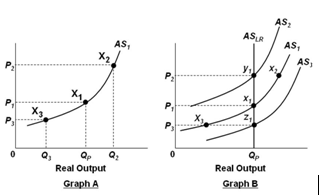
A. Lower nominal wages and a shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve from AS1 to AS2
B. Higher nominal wages and a shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve from AS1 to AS2
C. Lower nominal wages and a movement from equilibrium point x1 to equilibrium point x2
D. Higher nominal wages and a movement from equilibrium point x1 to equilibrium point x2