What is the largest tax in the United States?
What will be an ideal response?
The largest tax in the United States is the federal income tax. Since the late 1960s, the federal income tax has been between 6 and 10 percent of GDP, and it is currently right in the middle of that range.
You might also like to view...
Diseconomies of scale occur when
A) long-run average costs fall as a firm expands its plant size. B) long-run labor costs rise as a firm increases its output. C) short-run average costs rise as a firm expands its plant size. D) long-run average costs rise as a firm increases its output.
In the context of labor markets, shirking refers to:
A. the nonmonetary disadvantages of certain jobs. B. the neglecting or evading of work. C. the elimination of monitoring costs. D. any scheme where pay is directly related to worker output.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as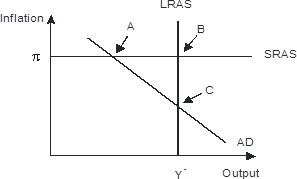
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
The meaning of interdependence in a monopolistically competitive market is
A. that firms will not take into account the reaction of rival firms. B. that it is difficult for firms to get together to collude. C. that price rigging commonly occurs. D. that products produced by firms will be good substitutes.