What is so difficult about making a working fusion reactor? Explain
What will be an ideal response?
There are quite a few: the electric repulsion of nuclei must be overcome; plasmas
exhibit instabilities that are tough to overcome; heat exchange is not trivial (liquid lithium is
not something to be toyed with); tritium production from lithium is a problem because
tritium is radioactive; inertial schemes require precise aiming; etc.
You might also like to view...
A 3.00 kg mass is located at x = 2.0 cm and y = 0.0. A 3.00 kg mass is located at x = 0.0 and y = 2.0 cm. A 4.00 kg mass is located at x = 3.0 cm and y = -3.0 cm. Where is the location of the center of mass?
A. (+1.8 cm, -0.60 cm) B. (+1.8 cm, +0.60 cm) C. (+0.60 cm, -1.8 cm) D. (+3.5 cm, -0.6 cm) E. (+1.8 cm, +1.6 cm)
Which one of the following statements concerning emf is true?
a) Emf is the work done in moving the current from one terminal to the other of an emf device. b) Emf is the work done in moving a single charge from one terminal to the other of an emf device. c) Emf is the force exerted on a single charge to move it from one terminal to the other of an emf device. d) Emf is the total charge moving from one terminal to the other of an emf device. e) Emf is the electromagnetic force that is exerted between the terminals of an emf device.
When a 27.0-? resistor is connected across a 4.50-V battery, a current of 473 mA flows. What is the resulting terminal voltage of the battery?
a. 30.7 V b. 6.86 V c. 12.8 V d. 57.1 V e. 0.537 V
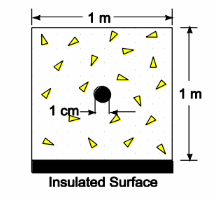
A long 1-cm-diameter electric cable is imbedded in a concrete wall (k = 0.13 W/(m K)) which is 1 m*1 m, as shown in the sketch. If the lower surface is insulated, the surface of the cable is 100°C and the exposed surface of the concrete is 25°C, estimate the rate of energy dissipation per meter of cable.
GIVEN
A long electric cable imbedded in a concrete wall with cable diameter (D) = 1 cm = 0.01 m
Thermal conductivity of the wall (k) = 0.13 W/(m K)
Wall dimensions are 1 m by 1 m, as shown in the sketch below
The lower surface is insulated
The surface temperature of the cable (Ts) = 100°C
The temperature of the exposed concrete surfaces (To) = 25°C
FIND
The rate of energy dissipation per meter of cable (q/L)
ASSUMPTIONS
The system is in steady state
The thermal conductivity of the wall is uniform
Two dimensional heat transfer
SKETCH