In the long run, all factors of production are
A) variable.
B) fixed.
C) materials.
D) rented.
A
You might also like to view...
If a used-car dealer enjoys economic profits, then
A) as a group, its customers necessarily suffered a like amount in economic losses. B) as a group, its customers were necessarily made worse off. C) as a group, its competitors necessarily suffered economic losses. D) all of the above are true. E) none of the above is true.
A firm produces in a perfectly competitive market and hires labor in a perfectly competitive labor market. The firm hires four workers, the marginal product of the fourth worker is 4, and the wage rate is $40 . The firm produces 100 units of the product, which sell for a price of $10 . This firm is
a. maximizing profit when it hires four workers b. not maximizing profit and should hire more workers to increase profit c. not maximizing profit and should hire fewer workers to increase profit d. not maximizing profit when it produces 100 units of the product and should increase production to increase profit e. not maximizing profit when it produces 100 units of the product and should decrease production to increase profit
Refer to the graph shown.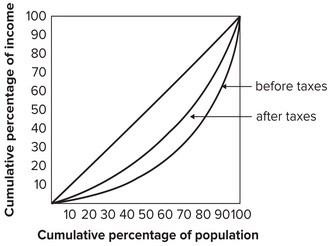 A possible explanation for the difference between the distribution of income before taxes and the distribution of income after taxes shown in the graph is that the tax system:
A possible explanation for the difference between the distribution of income before taxes and the distribution of income after taxes shown in the graph is that the tax system:
A. is progressive. B. is proportional. C. is regressive. D. does not affect income inequality.
A person buying a used car could ask the seller for permission to take the car to a mechanic for an inspection. If the seller says no, the prospective buyer has gained information about the car. This process is known as:
A. screening. B. internalizing the externality. C. licensing. D. signaling.