When demand is elastic, if we were to lower price, total revenue would ________; when demand is inelastic, if we were to lower price, total revenue would ________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
rise; fall
You might also like to view...
People combining the effects of past policy changes on important economic variables with their own judgment about the future effects of current and future policy changes is consistent with
A) frictional unemployment. B) the rational expectations hypothesis. C) active policy making. D) passive policy making.
Product differentiation
a. refers to the attempt of firms to make their goods look like those of the other firms in the industry b. refers to the attempt of firms to make essentially substitutable goods look different in the minds of the consumers c. refers to the advantage big firms have in research and development d. is a common characteristic of a perfectly competitive market structure e. is only employed in a monopoly market structure
Which of the following is not true?
A. George H.W. Bush won reelection after agreeing to a small tax increase as part of a political compromise. B. George W. Bush won election after claiming tax cuts would pay for themselves. C. Ronald Reagan claimed tax cuts would spur economic gains that would increase tax revenues before the tax cuts led to significantly lower revenues. D. After Bill Clinton raised taxes on upper income individuals to reduce federal budget deficits his party lost heavily in the following congressional elections.
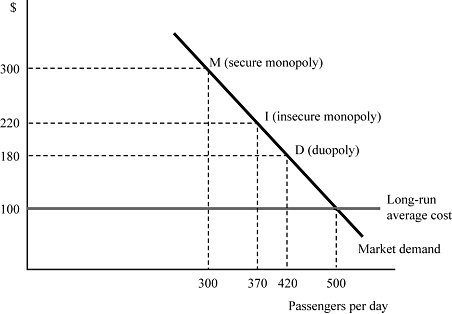
 In Figure 8.10, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit-maximizing price of $300 per ticket. Suppose that Fly Smart discovers that a second airline is contemplating entering the market. If the minimum market entry quantity is zero passengers per day, what is Fly Smart's profit when it commits to the entry-deterring quantity?
In Figure 8.10, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit-maximizing price of $300 per ticket. Suppose that Fly Smart discovers that a second airline is contemplating entering the market. If the minimum market entry quantity is zero passengers per day, what is Fly Smart's profit when it commits to the entry-deterring quantity?
A. $60,000 B. $44,400 C. $33,600 D. $0