What describes the graphical relationship between average product and marginal product?
A) Average product cuts marginal product from above, at the maximum point of marginal product.
B) Average product cuts marginal product from below, at the maximum point of marginal product.
C) Marginal product cuts average product from above, at the maximum point of average product.
D) Marginal product cuts average product from below, at the maximum point of average product.
E) Average and marginal product do not intersect.
C
You might also like to view...
Assume Joe invests a total of $10,000 in a company - $5,000 of which is his own money and $5,000 which he borrowed at a 10% interest rate. If the company's stock value increases by 20% in one year at which time Joe sells his shares of the stock, what is Joe's rate of return on his investment?
a. 10% b. 15% c. 20% d. 30%
If an investment has a 20% (0.20) probability of returning $1,000; a 30% (0.30) probability of returning $1,500; and a 50% (0.50) probability of returning $1,800; the expected value of the investment is:
A. $1,433.33 B. $1,600.00 C. $1,550.00 D. $2,800.00
Refer to the table. A decline in the international value of the dollar would:
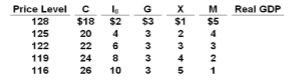
Answer the question on the basis of the following table for a particular country in which C is
consumption expenditures, I g is gross investment expenditures, G is government expenditures,
X is exports, and M is imports. All figures are in billions of dollars. Each question is
independent of other question using the same table, unless otherwise stated.
A. increase the values in columns (5) and (6) and reduce aggregate demand.
B. decrease the values in columns (5) and (6) and increase aggregate demand.
C. decrease the values in column (5), increase the values in column (6), and reduce
aggregate demand.
D. increase the values in column (5), decrease the values in column (6), and increase
aggregate demand.
Supply curves are generally _______ sloping because _______________.
A. downward; more consumers will buy the good if the price falls. B. upward; of the principle of increasing opportunity costs. C. downward; it is less expensive to mass produce goods. D. upward; of inflation.