A 10-kg object is dropped from rest. After falling a distance of 50 m, it has a speed of 26 m/s. What is the change in mechanical energy caused by the dissipative (air) resistive force on the object during this descent?
a. ?1.3 kJ
b. ?1.5 kJ
c. ?1.8 kJ
d. ?2.0 kJ
e. ?2.3 kJ
b
You might also like to view...
Compound Microscope: The objective lens and the eyepiece of a microscope have focal lengths of 4.0 mm and 25 mm, respectively. The objective produces a real image 30 times the size of the object, with the final image viewed at infinity. The near point of the microscope user is at 25 cm. What is the distance between the objective lens and the real image that it produces?
A. 116 mm B. 120 mm C. 124 mm D. 128 mm E. 132 mm
A 4.00 kg hollow sphere of radius 5.00 cm starts from rest and rolls without slipping down a 30.0 degree incline. If the length of the incline is 50.0 cm, then the velocity of the center of mass of the hollow sphere at the bottom of the incline is
A. 1.28 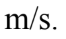
B. 1.44 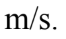
C. 1.65 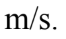
D. 1.72 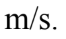
E. 1.98 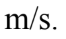
When two gases separated by a diathermal wall are in thermal equilibrium with each other:
A. it rises to the ceiling B. it sinks to the floor C. it stops expanding D. it starts to contract E. none of the above
An air conditioning unit is vibrating in simple harmonic motion with a period of 0.27 s and a range (from the maximum in one direction to the maximum in the other) of 3.0 cm. At t = 0 it is at its central position and moving in the +x direction
What is its position when t = 55 s? A) x = -0.430 cm B) x = -0.511 cm C) x = 0.511 cm D) x = -1.41 cm E) x = -1.44 cm