Draw individual demands for caviar for Al, Barbara, Chuck, and Denise where Al's demand is relatively inelastic, Barbara's is elastic, Chuck's is upward sloping, and Denise refuses to eat caviar at any price. Then draw the corresponding market demand
Figure 5-21
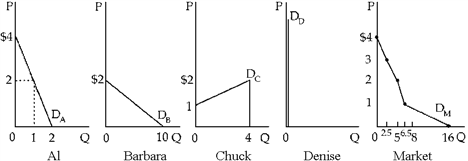
(See Figure 5-21). Al's demand is steep with respect to price, while Barbara's is relatively flat. Chuck's D slopes up with respect to price, while Denise consumes zero at all prices. Market demand is a horizontal summation of individual demands at quantities purchased by A, B, and C (D is zero). Market D will slope down unless Chuck has such a strong opposite relationship to offset the downward demands of both Al and Barbara.
You might also like to view...
What is the dominant strategy for Bob? Donna? Which strategy should each player choose to maximize the potential gain? What do you think the outcome of this game will be? Carefully explain your answers
What will be an ideal response?
The point where quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal is known as the
a. ceiling price. b. minimum price. c. equilibrium price. d. administered price.
A group price discriminator sells its product in Florida for three times the price it sets in New York. Assuming the firm faces the same constant marginal cost in each market and the price elasticity of demand in New York is -2
0, the demand in Florida A) has an elasticity of -6.0. B) is more price elastic than the demand in New York. C) has an elasticity of -1.2. D) has an elasticity of -0.67.
Contractionary fiscal policy is enacted when the overall effect of decisions about taxation and spending is to:
A. increase aggregate demand. B. increase aggregate supply. C. reduce aggregate demand. D. reduce aggregate supply.