When foreign countries buy wheat grown in the United States, they are generating a
A. Demand for U.S. dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
B. Demand for U.S. dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
C. Supply of U.S. dollars and a supply of a foreign currency.
D. Supply of U.S. dollars and a demand for a foreign currency.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A town wants to build a new bridge. Construction firms will submit sealed bids
The town will award the contract to the firm that submits the lowest bid and will pay the firm the amount of the second lowest bid (that is, the town will conduct a second-price procurement auction). So, for example, if Firm A bids $8 million, Firm B bids $9 million, and Firm C bids $10 million then the city will award the contract to Firm A (it submitted the lowest bid) and pay Firm A $9 million (the amount of the second lowest bid). Suppose your firm is willing to build the bridge for a minimum of $9 million. a. Show that bidding $9 million is a better strategy than bidding some amount below $9 million— say, $7 million. b. Show that bidding $9 million is a better strategy than bidding some amount above $9 million—say, $11 million.
What are the main features of the Harris-Todaro model of rural-urban migration?
What will be an ideal response?
Christina Romer's estimates of the business cycles prior to World War II showed that the business cycle
A) had greater fluctuations before World War II than previous estimates had shown. B) had smaller fluctuations before World War II than previously estimated. C) had smaller fluctuations before World War II than after World War II. D) had larger fluctuations after World War II than had been previously measured.
Refer to Figure 10.1. Suppose the individual is initially at point b. Based on the figure, the individual is currently:
}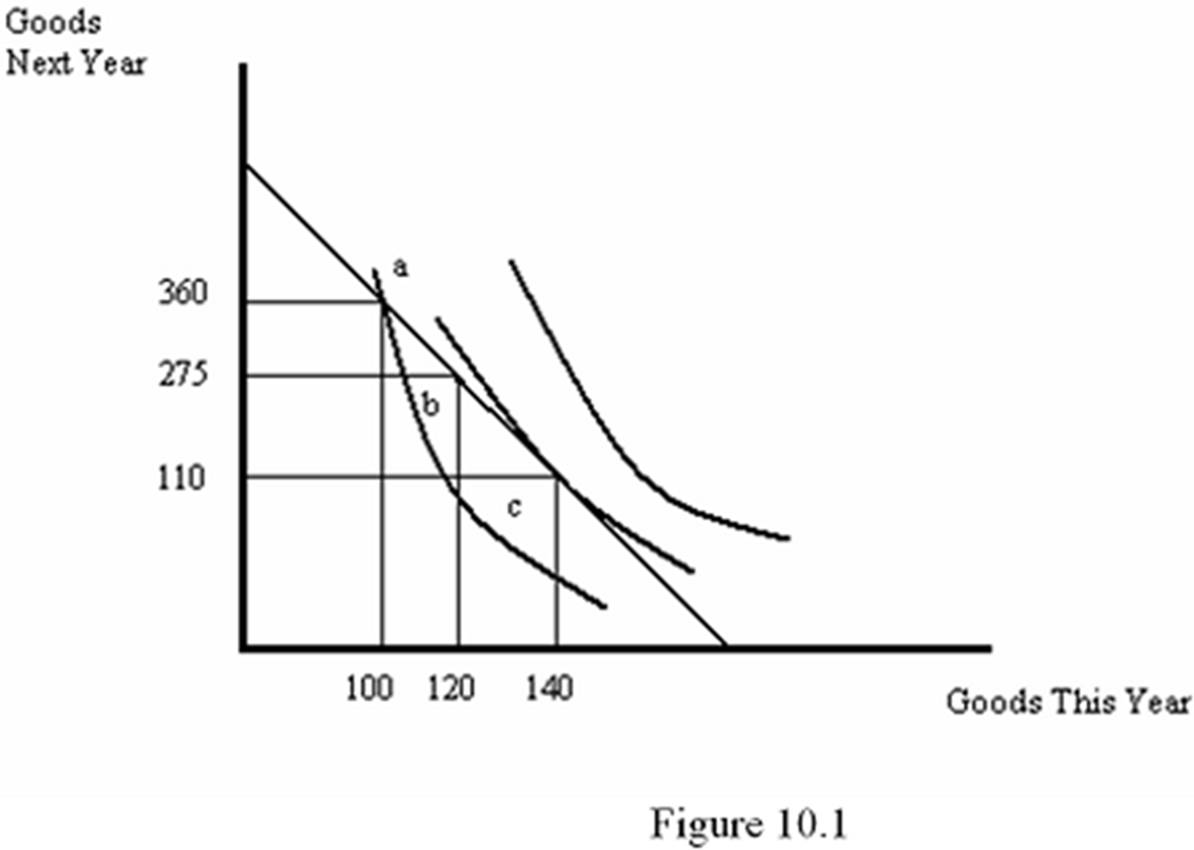
A. a saver, which is his optimal choice.
B. a borrower, which is his optimal choice.
C. a saver, though borrowing would increase his utility.
D. a borrower, though saving would increase his utility.