The adjustment in economic policy designed to counteract small changes in economic outcomes
A. Is the concept of fine-tuning.
B. Is the policy approach favored by most economists.
C. Is compatible with our design capabilities.
D. Has been easy to accomplish over the last decade.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The key issue with competition is the role competition plays in eliminating ________ and making the ________ as large as possible
A) cooperative surplus; profits B) producer surplus; consumer surplus C) deadweight losses; cooperative surplus D) shortages; total revenue
In a competitive market free of government regulation,
A. price adjusts until quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied. B. supply adjusts to meet demand at every price. C. price adjusts until quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied. D. price adjusts until quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
If the economy was producing at point X and moved to point Y,
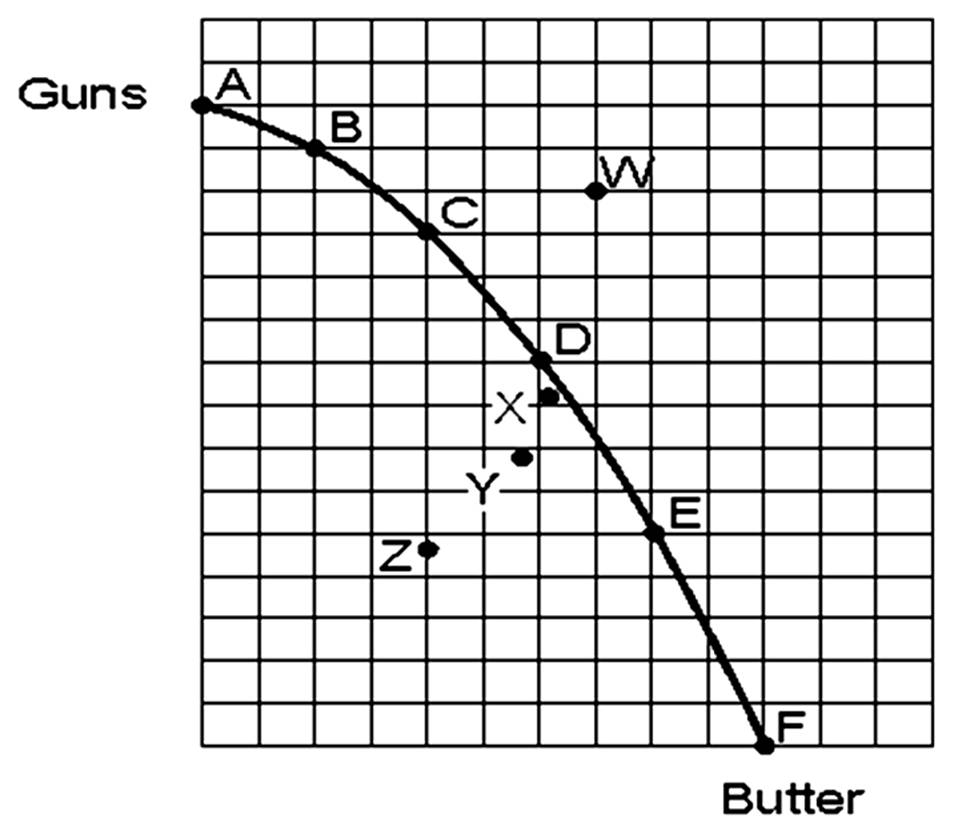
A. it would have moved from where the economy operates most of the time to a severe recession.
B. it would have moved from where the economy operates most of the time to a depression.
C. the unemployment rate would increase.
D. it would have moved from where the economy operates most of the time to a severe recession AND the unemployment rate would increase.
Suppose that Mexico and Canada both peg their currencies to the U.S. dollar. The relationship between the Mexican peso and the Canadian dollar is best described as a(n):
A) indirect peg. B) fixed exchange rate system. C) currency union. D) free trade area.