Any cost of negotiating or enforcing a contract is
a. an external cost.
b. a private cost.
c. a transaction cost.
d. a side payment.
c. a transaction cost.
You might also like to view...
________, in economics, refers to a preference for equal outcomes within the target population
A) Randomness B) Rationalism C) Fairness D) Liberalism
As the price of a good increases, the loss in consumer surplus is larger,
A) the more elastic demand is. B) the more money previously spent on the good. C) the less money previously spent on the good. D) the smaller the price increase.
A 10% increase in the price of pizza causes a 10% drop in the quantity of both pizza and beer sold. Describe elasticities and the nature of the two products.
a. The price elasticity of demand for pizza is equal to 1 and the cross price elasticity of beer with respect to the price of pizza is also 1. In this example, beer and pizza complements. b. The price elasticity of demand for pizza is equal to 1 and the cross price elasticity of beer with respect to the price of pizza is (-)1. In this example, beer and pizza complements. c. The price elasticity of demand for pizza is equal to (-)1 and the cross price elasticity of beer with respect to the price of pizza is 1. In this example, beer and pizza complements. d. The price elasticity of demand for pizza is equal to (-)1 and the cross price elasticity of beer with respect to the price of pizza is also (-)1. In this example, beer and pizza complements.
Use the indifference curves and the budget lines in Figure 19.3 to answer the indicated question. Assume the price of Y is $1 per unit. If the price per unit of good X is $3, the consumer would maximize utility at point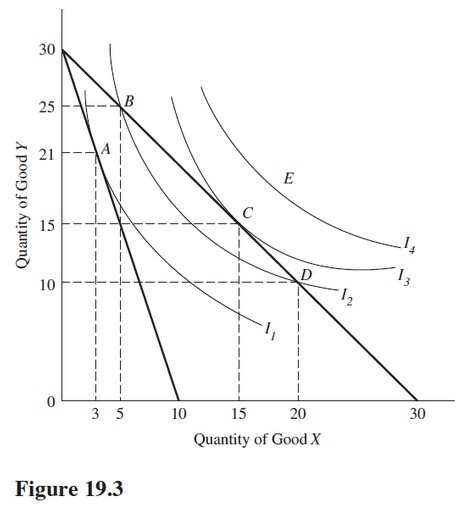
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.